Work class 9
Work class 9
Work is said to be done if force is applied to a body and it displaces in the direction of applied force.
Work done (W) by a constant force (F) after displacing a body to a distance ‘d’-
W = F d cosθ
Where θ is the angle between force and displacement.
Work is a scalar quantity.
Unit of work:
SI unit of work is joule (J).
CGS unit of work is erg.
1 J = 10⁷ erg
Types of Work:
Positive work:
If Force and displacement both are in same direction positive work is done.
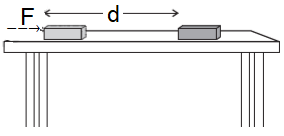
In the above example, a constant force ‘F’ is applied to a brick kept on a smooth horizontal table. The brick is displaced to a distance ‘d’ in the direction of the applied force . The work done by the applied force will be
W = F d cosθ
Here, the angle between the applied force and displacement is θ = 0˚, as both are in the same direction. So, cosθ = cos0˚ = 1
W = F d
Work = Force × Displacement
Negative work:
If Force and displacement both are in opposite direction negative work is done.
- Example of negative work-
- Work done by frictional force is always negative.
- Work done by gravitational force while upward journey of body is negative.
Zero work:
If Force and displacement both are perpendicular to each other there is no work or zero work.
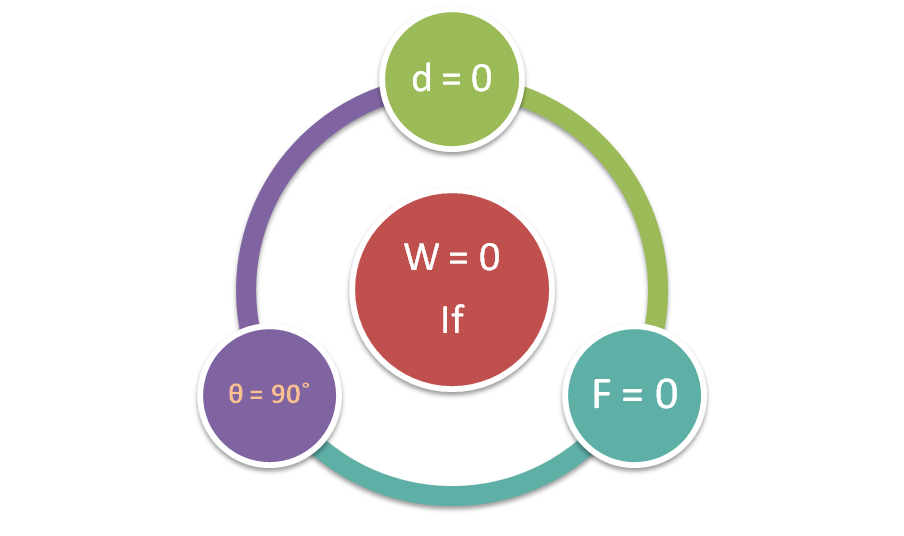
- Work done may be zero if,
- Displacement is zero (d = 0).
- Force zero (F = 0).
- Angel between force and displacement are perpendicular to each other (θ = 90˚).
Energy
The ability to do work is called energy.
Energy is a scalar quantity.
Unit of Energy:
The SI unit of energy is called joules (J).
Types of energy:
- Mechanical energy
- Kinetic energy
- Potential energy
- Thermal energy
- Chemical energy
- Solar energy
- Nuclear energy
MY YouTube Channel Link : 👉🖱 https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCGpC7nWE0-bBv9I53MM8