What is Rectifier?
Rectifier is a device which is used to convert alternate current to direct current and the process is called rectification.

Rectifier Principle:
It works on the principle that when a pn-junction diode is in forward bias it offers low resistance and current passes through it, but when it is in reverse bias it offers high resistance and almost no current flow through it. This property of diode is used to rectify alternate current.
Uses of Rectifiers:
- Rectifiers are used in a wide range of electronic applications,
- in power supplies
- in battery chargers
- in audio amplifiers
- in motor control circuits
- in household appliances, such as televisions and refrigerators.
Types of Rectifiers:
Rectifiers are of two types,
- Half wave rectifier
- Full wave rectifier
Table of Contents
Half wave Rectifier
Half wave Rectifier consists of a transformer, a junction diode D and a load resistance RL. Transformer lowers voltage, diode rectifies it and output is obtained across load resistance.
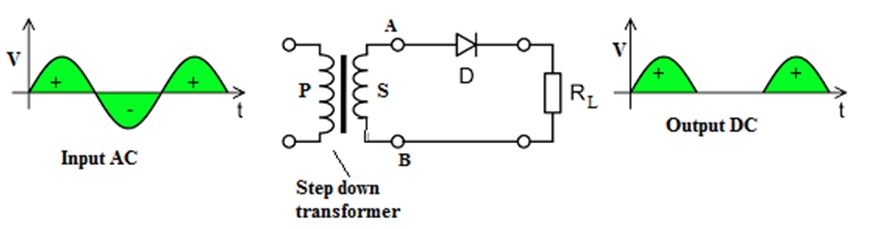
Working of Half wave Rectifier:
When positive half cycle of AC is applied to end A, and at same time end B is negative. The diode D is in forward bias and current is obtained through RL; output wave form is same as positive half cycle of input AC. During negative half cycle of applied voltage end A becomes negative and B positive. The diode is in reverse biased and no current flows; no voltage appears across RL. In the next positive half cycle, again we get output voltage which is unidirectional and pulsating.
Note: In half wave rectifier the frequency of input and output signal is same.
Full wave Rectifier
A full wave rectifier is an electronic circuit that converts an alternating current (AC) input signal into a direct current (DC) output signal. It is designed to rectify both the positive and negative halves of the AC signal, resulting in a more steady DC output.
It consists of a centre tap transformer, two junction diodes D1 and D2 and a load resistance RL. p–end of both junction diodes D1 and D2 are connected to secondary coil of transformer and n-end of both diode is connected to centre tap of transformer T with a load resistance RL.
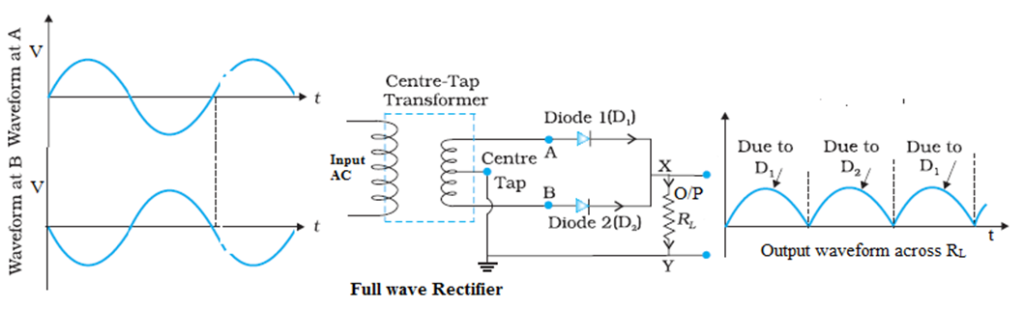
Working of Full wave Rectifier:
During the positive half cycle of AC input, end A is positive and end B is negative with respect to the centre tap T. Then diode D1 gets forward bias and conducts current along path AD1XYTA. During same time diode D2 is in reverse bias and does not conducts current. During the negative half cycle of AC input, end B is positive and end A is negative with respect to the centre tap T. Then diode D2 gets forward bias and conducts current along path BD2XYTB. During same time diode D1 is in reverse bias and does not conducts current.
During both half cycles current have same sense along RL so a pulsating unidirectional current is obtained along RL.
Note: In full wave rectifier the frequency of output signal is double as that of input signal as two ripples are obtained in one cycle of input.
Difference between Half Wave Rectifier and Full Wave Rectifier
| S.No. | Half wave rectifier | Full wave rectifier |
| 1. | Only one diode is used | Two diodes is used |
| 2. | Ordinary transformer is used | Centre tap transformer is used |
| 3. | only alternate half cycles of applied alternating signal are converted into direct current | Whole cycle of applied alternating signal is converted into direct current. |
| 4. | Rms value of current Irms= Io / 2 | Rms value of current Irms=Io / (√2) |
| 5. | Idc = Io/π | Idc = 2 Io/π |
| 6. | Value of dc component is less than ac in output | Value of dc component is more than ac in output |
| 7. | It’s efficiency is about 40.6% | It’s efficiency is about 81.2% |
Important questions from the Topic
What is a rectifier?
A rectifier is an electronic device that converts alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC). It does this by allowing current to flow in only one direction through a circuit, typically using a diode or a series of diodes.
What are the types of rectifiers?
There are two main types of rectifiers: half-wave and full-wave. A half-wave rectifier only allows current to flow in one direction during half of the AC cycle, while a full-wave rectifier allows current to flow in one direction during the entire cycle.
What are the applications of a half wave rectifier?
Ans: Its most common applications are voltage multipliers, battery chargers, and low-power DC power supplies.
What is a half wave rectifier?
Ans: It is a circuit that converts an AC voltage into a pulsating DC voltage by allowing only one-half cycle of the input waveform to pass through and blocking the other half.
What are the advantages of using a full wave rectifier?
Ans: The advantages of using a full wave rectifier include a higher DC output voltage, improved efficiency, and reduced ripple in the output signal. This makes it ideal for use in power supply circuits and other applications where a steady and reliable DC voltage is required.
How does a rectifier work?
A rectifier works by using a diode or series of diodes to block current flow in one direction during the negative half-cycle of an AC input signal. During the positive half-cycle, the diode(s) conduct and allow current to flow in the forward direction. This results in a pulsating DC output signal that can be smoothed out with a filter capacitor.
What are the disadvantages of using a full wave rectifier?
Ans: The main disadvantage of using a full wave rectifier is that it requires more components than a half wave rectifier, making it slightly more complex and expensive. Additionally, the circuit can produce electromagnetic interference (EMI) which can affect nearby electronic devices.
How does a half wave rectifier work?
Ans: A half wave rectifier works by using a diode to block the negative half of the AC input signal and pass only the positive half. The diode is connected in series with the load resistor and the input voltage source. During the positive half cycle of the input voltage, the diode conducts, allowing the current to flow through the load resistor, resulting in a positive voltage across it. During the negative half cycle, the diode blocks the current flow, resulting in no voltage across the load resistor.
What is the output waveform of a half wave rectifier?
Ans: The output waveform of a half wave rectifier is a pulsating DC waveform that consists of a series of positive half cycles of the input waveform with no negative half cycles.
What are the advantages of a half wave rectifier?
Ans: The advantages of a half wave rectifier include its simplicity, low cost, and ease of implementation.
What are the disadvantages of a half wave rectifier over full wave rectifier?
Ans: The disadvantages of a half wave rectifier include its low efficiency, as only half of the input waveform is used to produce the output, and the presence of significant ripple in the output waveform, which may require additional filtering to smooth out.
What is a full wave rectifier?
Ans: A full wave rectifier is an electronic circuit that converts an alternating current (AC) input signal into a direct current (DC) output signal. It is designed to rectify both the positive and negative halves of the AC signal, resulting in a more steady DC output.
How does a full wave rectifier work?
Ans: A full wave rectifier works by utilizing two diodes that are connected in a “bridge” configuration. This allows the AC signal to be rectified in both the positive and negative halves, resulting in a DC output that has a higher average voltage than a half wave rectifier.
What are the advantages of using a full wave rectifier?
Ans: The advantages of using a full wave rectifier include a higher DC output voltage, improved efficiency, and reduced ripple in the output signal. This makes it ideal for use in power supply circuits and other applications where a steady and reliable DC voltage is required.
What are the disadvantages of using a full wave rectifier?
Ans: The main disadvantage of using a full wave rectifier is that it requires more components than a half wave rectifier, making it slightly more complex and expensive. Additionally, the circuit can produce electromagnetic interference (EMI) which can affect nearby electronic devices.
What is a half wave rectifier?
Ans: A half wave rectifier is a circuit that converts an AC voltage into a pulsating DC voltage by allowing only one-half cycle of the input waveform to pass through and blocking the other half.
What is the difference between a full wave rectifier and a half wave rectifier?
Ans: The main difference between a full wave rectifier and a half wave rectifier is that the full wave rectifier can rectify both the positive and negative halves of an AC signal, while the half wave rectifier only rectifies the positive half. This results in a higher average DC output voltage and reduced ripple in the output signal for the full wave rectifier.
What are the disadvantages of a half wave rectifier?
Ans: The disadvantages of a half wave rectifier include its low efficiency, as only half of the input waveform is used to produce the output, and the presence of significant ripple in the output waveform, which may require additional filtering to smooth out.
How does a rectifier work?
A rectifier works by using a diode or series of diodes to block current flow in one direction during the negative half-cycle of an AC input signal. During the positive half-cycle, the diode(s) conduct and allow current to flow in the forward direction. This results in a pulsating DC output signal that can be smoothed out with a filter capacitor.
What is the efficiency of a rectifier, and how is it calculated?
The efficiency of a rectifier is the ratio of the DC output power to the AC input power, expressed as a percentage.
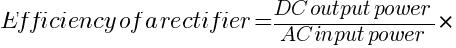 100%
100%
What is ripple voltage, and how is it reduced in a rectifier circuit?
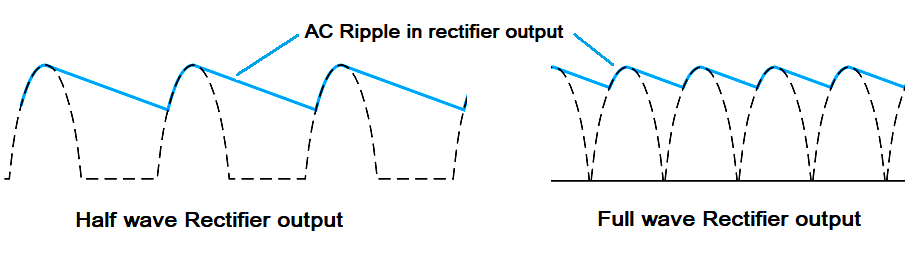
Ripple voltage is the AC component of the output voltage of a rectifier circuit. It is caused by the fact that the rectifier only allows current to flow in one direction, resulting in a pulsating DC output. Ripple voltage can be reduced by adding a filter capacitor to the output of the rectifier, which smooths out the output voltage.
What is a bridge rectifier?
A bridge rectifier is a type of full-wave rectifier that uses four diodes arranged in a bridge configuration to rectify AC input signals. This configuration provides a more efficient and higher voltage DC output than a half-wave rectifier.
What is the difference between a center-tapped and a bridge rectifier?
A center-tapped rectifier uses a transformer with a center-tapped secondary winding to create a voltage source that is split into two equal parts, with each half providing an AC voltage. A diode is placed between each half and the load, allowing current to flow in only one direction. A bridge rectifier, on the other hand, uses four diodes arranged in a bridge configuration to rectify the AC input signal.
What are some common applications of rectifiers?
Rectifiers are used in a wide range of electronic applications, including power supplies, battery chargers, audio amplifiers, and motor control circuits. They are also used in household appliances, such as televisions and refrigerators.
What is the difference between a rectifier and an inverter?
A rectifier converts AC to DC, while an inverter converts DC to AC. Inverters are commonly used in solar power systems, electric vehicles, and uninterruptible power supplies (UPS) to convert DC power from a battery or other source into AC power for use in homes or businesses.
What are the disadvantages of a half wave rectifier?
Ans: The disadvantages of a half wave rectifier include its low efficiency, as only half of the input waveform is used to produce the output, and the presence of significant ripple in the output waveform, which may require additional filtering to smooth out.
What are the applications of a half wave rectifier?
Ans: The applications of a half wave rectifier include voltage multipliers, battery chargers, and low-power DC power supplies.
Can a single semiconductor material be doped with both n-type and p-type dopants simultaneously? If so, what is the resulting material called?
Yes, a semiconductor material brick can be doped with both n-type and p-type dopants simultaneously side-by-side. This creates a material known as a semiconductor junction or a p-n junction, which has unique electrical properties that are useful for electronic device applications.
How do the properties of a doped semiconductor material affect the behavior of electronic devices made from it, such as diodes and transistors?
The properties of a doped semiconductor material play a critical role in determining the behavior of electronic devices made from it. For example, the doping concentration can affect the conductivity and resistance of a material, while the type of dopant can affect its optical and thermal properties.
Manav Sampda Par Avkash Sambandhi Niyam
What is Rectifier?, What is Rectifier?, What is Rectifier?, What is Rectifier?, What is Rectifier?, What is Rectifier?, What is Rectifier?, What is Rectifier?, What is Rectifier?, What is Rectifier?, What is Rectifier? What is Rectifier?, What is Rectifier?, What is Rectifier?, What is Rectifier?, What is Rectifier?, What is Rectifier?, What is Rectifier?
What is Rectifier?, What is Rectifier?, What is Rectifier?, What is Rectifier?, What is Rectifier? What is Rectifier?, What is Rectifier?, What is Rectifier?, What is Rectifier?, What is Rectifier?, What is Rectifier?, What is Rectifier?, What is Rectifier?, What is Rectifier?, What is Rectifier?, What is Rectifier?, What is Rectifier? What is Rectifier?