What is a Photocell?
Table of Contents
What is a Photocell?
What is a Photocell?
A photocell is a device whose electrical conductivity changes when light falls on it. A photocell is also known as an electric eye. (What is a Photocell?)
Principle: It works on the basis of photoelectric effect.
Working: When light of a suitable wavelength falls on the emitter C, photoelectrons are emitted. A change in the intensity of falling radiation changes the number of photoelectrons and hence the photocurrent.
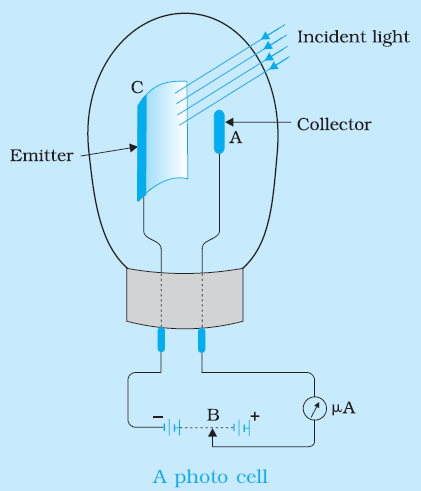
Applications of photocells:
Photocells are widely used in a variety of applications due to their ability to detect light and respond by changing their electrical resistance. Some common uses of photocells include:
(1) Light control: Photocells are used in streetlights, outdoor lighting, and building lighting systems to turn lights on and off based on the amount of light present in the environment.
(2) Photographic cameras: Photocells are used in photographic cameras to measure the ambient light level and adjust the flash intensity accordingly.
(3) Solar panels: Photocells are an essential component of solar panels, where they convert light into electricity to power homes, businesses, and other applications.
(4) Automation: Photocells are used in automation systems to detect the presence or absence of light and trigger specific actions, such as turning on or off a motor or activating an alarm, automatic door openers, and burglar alarms.
(5) Robotics: Photocells can be used in robotics to detect changes in light levels and respond accordingly, such as adjusting the speed of a motor or changing the direction of movement.
Important questions from Photocell
What is a photocell?
Ans: A photocell is an electronic device that converts light energy into electrical energy. It is also known as a photoelectric cell or a photovoltaic cell.
How does a photocell work?
Ans: A photocell works by using the photoelectric effect to convert light energy into electrical energy. When light hits the surface of the photocell, it ejects electrons from the material, which creates an electrical current.
What are the components of a photocell?
Ans: The main components of a photocell include a photo-emissive material, which is the material that emits electrons when it is exposed to light, and a metal electrode, which collects the emitted electrons to create an electrical current.
What are some common applications of photocells?
Ans: Photocells have a wide range of applications, including in solar panels, light sensors, light meters, automatic door openers, and burglar alarms. They are also used in scientific research to measure the properties of light and to study the photoelectric effect.
What is the photoelectric effect?
Ans: The photoelectric effect is the phenomenon in which electrons are ejected from a material when it is exposed to light. This effect was first observed by Hertz in 1887 and later explained by Einstein in 1905 as a fundamental principle of quantum mechanics.
What are the advantages of using photocells in energy generation?
Ans: The advantages of using photocells in energy generation include their low cost, reliability, and environmental friendliness. Photocells do not emit any greenhouse gases or other pollutants and can be used in a wide range of applications, from small-scale solar panels to large-scale power plants.
What are the disadvantages of using photocells in energy generation?
Ans: The disadvantages of using photocells in energy generation include their relatively low efficiency, which means that they currently cannot generate as much power as other forms of energy generation, such as fossil fuels or nuclear power. Additionally, photocells require a significant amount of space and may not be suitable for all environments or climates.
What is a Photocell?