There is a uniform spherically symmetric surface charge density at a distance R0 from the origin.
Question 1:
There is a uniform spherically symmetric surface charge density at a distance R0 from the origin. The charge distribution is initially at rest and starts expanding because of mutual repulsion. The figure that represents best the speed V(R(t)) of the distribution as a function of its instantaneous radius R(t) is
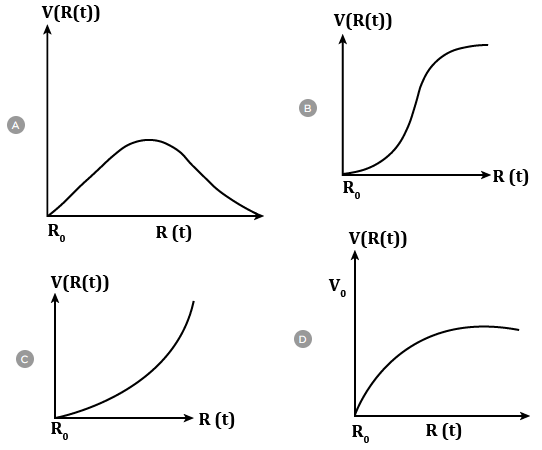
Solution:
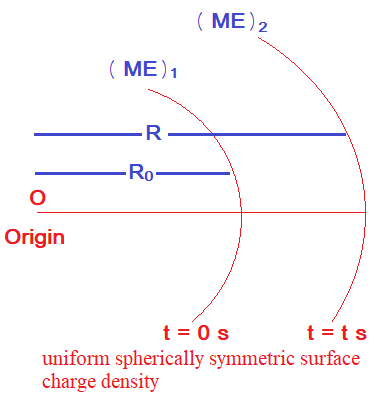
Since uniformly charge distributed surface expands due to mutual repulsion, without influence of external agency. So, energy will be conserved in this process.
From law of conservation of energy,
Mechanical energy initial (t = 0 second) = Mechanical energy final (t = t second)
(KE)1 + (Electrostatic PE)1 = (KE)2 + (Electrostatic PE)2
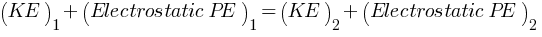
![{1/2 mv^2} = kQ^2 / 2 + [1/R_0 - 1/R] {1/2 mv^2} = kQ^2 / 2 + [1/R_0 - 1/R]](https://mywebpathshala.com/wp-content/plugins/wpmathpub/phpmathpublisher/img/math_971_243427f78940752376c37e17b57be645.png)
![v = sqrt{kQ^2 / m + [1/R_0 - 1/R]} v = sqrt{kQ^2 / m + [1/R_0 - 1/R]}](https://mywebpathshala.com/wp-content/plugins/wpmathpub/phpmathpublisher/img/math_971_9bc8af4600e777b2c051112758ff1f5d.png)
here, k, Q, m and R0 are constant terms so the speed (v) with which charge distribution expands depends only on R and
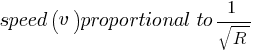
i.e. ‘v’ decreases with increase in R
Here, it is observed in option D only so ‘D’ is correct
Questions related to Topic
What is charge density and how is it defined?
Charge density is a measure of the amount of electric charge per unit volume or per unit area of a surface. It is defined as the amount of charge contained within a certain volume or surface area.
What is the SI unit of charge density?
The SI unit of charge density depends on whether it is volumetric or surface charge density. For volumetric charge density, the unit is coulombs per cubic meter (C/m³), while for surface charge density, the unit is coulombs per square meter (C/m²).
How does charge density affect electric field strength?
Charge density is directly proportional to the electric field strength. In other words, the greater the charge density, the stronger the electric field in the region around the charge.
How is charge density related to the Coulomb force?
The Coulomb force is the force of attraction or repulsion between two charged particles. The magnitude of the Coulomb force is directly proportional to the product of the charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. Charge density is related to the Coulomb force because it affects the strength of the electric field, which in turn affects the force experienced by a charged particle.
What is the difference between volumetric charge density and surface charge density?
Volumetric charge density is the amount of charge per unit volume of a material, while surface charge density is the amount of charge per unit area of a surface. In other words, volumetric charge density refers to the charge contained within a given volume, while surface charge density refers to the charge contained on a given surface area.
How can charge density be calculated for a given system?
Charge density can be calculated by dividing the total charge of a system by its volume or surface area, depending on whether it is volumetric or surface charge density.
How does charge density vary in different materials?
Charge density can vary significantly depending on the material properties and the presence of charged particles or ions. For example, metals tend to have a higher charge density than insulators due to the presence of free electrons that can move around and contribute to the overall charge density.
How does charge density relate to the concept of capacitance?
Capacitance is a measure of a system’s ability to store electric charge. Charge density is directly proportional to the capacitance of a system because the more charge that can be stored in a given volume or area, the greater the capacitance of the system.
How is charge density used to describe the behavior of charged particles in a magnetic field?
Charge density can be used to calculate the current density of a charged particle moving through a magnetic field. This current density, in turn, affects the magnetic field strength and the force experienced by the charged particle.
What is the effect of charge density on the electrical potential energy of a system?
Charge density affects the electrical potential energy of a system because the amount of energy stored in an electric field is directly proportional to the charge density. The higher the charge density, the greater the amount of potential energy stored in the electric field.
There is a uniform spherically symmetric surface charge density …..
Activities Supporting Speaking Skill Development