THE FUNDAMENTAL UNIT OF LIFE NCERT in-text Solutions Chapter-05
Table of Contents
THE FUNDAMENTAL UNIT OF LIFE NCERT in-text Solutions page 59
Question 1:
Who discovered cells, and how?
Answer: Robert Hooke first discovered cells in 1665. He observed the cells in a cork slice with the help of a self designed primitive microscope.
Question 2:
Why is the cell called the structural and functional unit of life?
Answer: The cell is called the structural and functional unit of life because every organism is made up of cells. Each living cell has the capacity to perform certain basic functions like producing energy, making new material in the cell, repairing the cell, clearing up the waste material from the cell, and so on that are essential functions of all living organisms.
THE FUNDAMENTAL UNIT OF LIFE NCERT in-text Solutions page 61
Question 1:
How do substances like CO2 and water move in and out of the cell? Discuss.
Ans: Substances like carbon dioxide move across the cell membrane by a process called diffusion. When a substance like CO2 accumulates (produced in the cell by burning glucose) in high concentrations inside the cell as compared to outside the cell, As soon as there is a difference in the concentration of CO2 inside and outside a cell, CO2 moves out of the cell, from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration outside the cell by the process of diffusion.
Water also obeys the law of diffusion and moves in a similar way as CO2. The movement of water molecules inside and outside the cell is done through a selectively permeable membrane across a concentration gradient. This process is known as osmosis.
- Concept ☞ Diffusion: The spontaneous movement of a substance from a region of its higher concentration to a lower concentration is called diffusion.
- Osmosis: Osmosis is the diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane from its higher concentration to a lower concentration.
Question 2:
Why is the plasma membrane called a selectively permeable membrane?
Ans: The plasma membrane allows or permits the entry and exit of some materials in and out of the cell while preventing the movement of some other materials. That’s why the plasma membrane is known as a selectively permeable membrane.
THE FUNDAMENTAL UNIT OF LIFE NCERT in-text Solutions page 63
Question 1:
Fill in the gaps in the following table illustrating differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
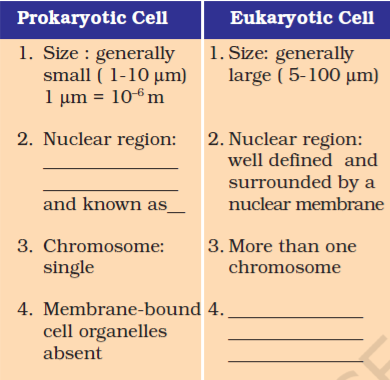
Answer:
| Sr. No. | Prokaryotic cell | Eukaryotic cell |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Size: generally small (1-10 µm). 1µm = 10-6m | Size: generally large (5-100 µm) |
| 2 | Nuclear region: poorly defined because of absence of a nuclear membrane and is known as Nucleoid. | Nuclear region: well-defined and surrounded by a nuclear membrane. |
| 3 | Chromosome: single. | More than one chromosome. |
| 4 | Membrane bound cell-organelles are absent. | Membrane bound cell-organelles such as mitochondria, plastids etc., are present. |
THE FUNDAMENTAL UNIT OF LIFE NCERT in-text Solutions page 65
Question 1:
Can you name the two organelles we have studied that contain their own genetic material?
Ans: Two organelles we have studied that contain their own genetic material are mitochondria and plastids.
Question 2:
If the organisation of a cell is destroyed due to some physical or chemical influence, what will happen?
Ans: If the organisation of a cell is destroyed due to some physical or chemical influence, then the cell will not be able to perform the basic functions like respiration, excretion, nutrition, etc., which are essential for life. Prohibition of such function leads to the death of the cell.
Question 3:
Why are lysosomes known as suicide bags?
Answer: When the cell gets damaged, lysosomes (which contain powerful digestive enzymes capable of breaking down all organic material) burst, and the enzymes digest their own cell. That’s why lysosomes are also known as the “suicide bags” of a cell.
Question 4:
Where are proteins synthesized inside the cell?
Answer: Ribosomes are the sites of protein synthesis. Ribosomes are present on the surface of the Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER).
THE FUNDAMENTAL UNIT OF LIFE NCERT in-text Solutions, THE FUNDAMENTAL UNIT OF LIFE NCERT in-text Solutions
MY YouTube Channel Link : 👉🖱 https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCGpC7nWE0-bBv9I53MM8qjQ