Speed and Velocity
Speed:
- Total distance covered by a body divided by time taken by it is called speed.
- Speed = Distance / Time taken
- SI Unit of speed is meter/second (m/s).
- Speed is a scalar quantity.
Table of Contents
Instantaneous speed:
- The speed of a body at a particular moment is called instantaneous speed. The instantaneous speed of a body is equal to the speed of that body at that moment in which we are observing it.
- Speedometer of a vehicle measures instantaneous speed and Odometer is used to measure total distance travelled by body.

Average speed:
- The average speed of a body is equal to the total distance travelled by the body divided by the total time taken by it on its entire journey.
- Average speed = Total distance travelled / Total time taken , this formula is true in all conditions and have no limit.
- Average speed = (speed 1 + speed 2) / 2 = (v1 + v2) / 2 , But this formula is applicable only when the body moves for the same time (t) with velocity v1 and v2.
Velocity:
- Total displacement covered by body divided by time taken by it called velocity.
- Velocity = Displacement / Time taken
- Velocity = (final position – initial position) / time taken
- SI Unit of velocity is meter/second (m/s)
- Velocity is a vector quantity.
Relative Velocity:
Velocity of a body with respect to another body is called relative velocity.

Example 1:
A man goes from Agra to Delhi, a distance of 250 km by bus in 5 hours. He stayed there an hour for shopping and came back by train in 4 hours. Calculate the speed of man for the entire journey.
Ans: Total distance travelled by man = 250km + 250km = 500km
Total time taken = 5 + 1 + 4 = 10hour
Average speed = Total distance travelled / Total time taken = 500km / 10hour = 50km/h
Example 2:
A tourist residing in Agra wants to visit Sariska National Park, Rajasthan, located at a distance of 180 km from Agra. He started his car at 6:00 a.m. and reached the national park at 9:00 a.m. For some reason, the national park was closed that day. He returns immediately and reaches Agra at 1:00 pm. Calculate the speed of the tourist’s forward and reverse journey. Also compute the speed of the entire journey.
Ans: Speed of tourist in forward journey (Agra to Rajasthan) = Distance travelled / Time taken = 180 / 3 = 60km/h
Speed of tourist in reverse journey (Agra to Rajasthan) = Distance travelled / Time taken = 180 / 4 = 45km/h
Speed of tourist in entire journey = Total distance travelled / Total time taken = (180 + 180) / 7 = 360/7 = 51.42km/h
👉❌ We can not calculate speed using formula vav = (v1 + v2) / 2 = (60 + 45) / 2 = 52.5km/h ❌ as journey time is not same for the both speed.
Example 3:
A motorcyclist drives from A to B with a uniform speed of 30 km/h and returns back with a speed of 20km/h. Find its average speed.
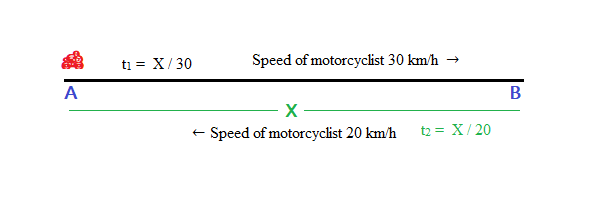
Ans: From A to B
Distance = X
Speed of motorcyclist 30 km/h
Time taken by motorcyclist t1 = distance / speed = X / 30
From B to A
Distance = X
Speed of motorcyclist 20 km/h
Time taken by motorcyclist t2 = distance / speed = X / 20
Average speed of motorcyclist for entire journey (from A to B and B to A) = total distance / Time taken
= ( X + X ) / t1 + t2 = 2X / ( X / 30 + X / 20 ) = 24km/h
Note: In above problem you can not use formula Average speed = ( V1 + V2 ) / 2 Because time is different for both journey. If a body moves with different velocity V1 and V2for same interval of time t and t then only we can use formula Average speed = ( V1 + V2 ) / 2
MY YouTube Channel Link : 👉🖱 https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCGpC7nWE0-bBv9I53MM8qjQ
Pages
Speed and Velocity, Speed and Velocity, Speed and Velocity, Speed and Velocity, Speed and Velocity, Speed and Velocity, Speed and Velocity, Speed and Velocity, Speed and Velocity, Speed and Velocity, Speed and Velocity, Speed and Velocity, Speed and Velocity, Speed and Velocity, Speed and Velocity