Semiconductor Electronics Class 12
Hello, readers! Here you will learn about basic concepts of semiconductor physics and some semiconductor devices like junction diodes and bipolar junction transistors. A few circuits illustrating their applications will also be discussed. Semiconductor Electronics materials devices and simple circuits
Table of Contents
Semiconductor Electronics materials devices and simple circuits
Semiconductor electronics involves the creation and application of electronic devices using semiconductor materials. Semiconductors possess characteristics that lie between conductors (allowing electric current) and insulators (blocking electric current).
Semiconductor electronics has brought about a technological revolution, enabling the creation of vital devices like transistors, diodes, and integrated circuits (ICs). These components form the backbone of contemporary electronic systems like computers, smart-phones, and televisions. Semiconductor electronics has led to the production of smaller, more efficient, and powerful devices, all while lowering costs. It has ushered in new opportunities in communication, transportation, medicine, and various other fields of human pursuit.
In field of Semiconductor electronics, semiconductors like silicon and germanium are predominantly used due to their favorable properties.
Materials:
- Silicon (Si): Silicon is the most widely used semiconductor material in electronics due to its abundance and excellent electrical properties. It forms the basis of many electronic components and integrated circuits.
- Germanium (Ge): Germanium was one of the earliest materials used in semiconductor electronics, but it has been largely replaced by silicon. However, germanium still finds limited applications, particularly in specialized devices.
Semiconductor Devices:
- Diode: A diode is a two-terminal electronic device that allows current to flow in only one direction. It consists of a P-N junction, formed by joining a P-type semiconductor (excess of holes) and an N-type semiconductor (excess of electrons).
- Transistor: A transistor is a three-terminal device that amplifies or switches electronic signals and forms the building block of modern electronic devices. Common types include bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) and field-effect transistors (FETs).
- Integrated Circuit (IC): An integrated circuit is a miniaturized electronic circuit that consists of interconnected semiconductor devices and passive components (resistors, capacitors, etc.) fabricated on a single chip of semiconductor material.
Simple Circuits:
- Rectifier Circuit: A rectifier circuit converts alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC) by using diodes to allow current flow in one direction.
- Amplifier Circuit: An amplifier circuit increases the amplitude of a weak signal, typically using transistors to provide amplification.
- Logic Gates: Logic gates are circuits that perform basic logic operations (AND, OR, NOT, etc.) on binary signals (0s and 1s) to perform digital computations.
- Oscillator Circuit: An oscillator circuit generates continuous waveforms, such as sine waves or square waves, which are crucial for generating timing signals in electronic systems.

Semiconductor Electronics Contents
Types of semiconductors 👉🖱 : Intrinsic Semiconductor and Extrinsic Semiconductor
Forward and reverse bias I-V characteristics of a pn-junction diode
👉🖱 Rectifier : Half wave rectifier and Full wave rectifier / Filter Circuits
👉🖱 Reverse Breakdown of junction diode: Zener breakdown & Avalanche breakdown
Zener diode / Zener diode as a Voltage Regulator
Optoelectronic junction devices / Photodiode / Light emitting diode (LED) / Solar cell

Classification of Solids on the basis of their Conductivity and Resistivity
| Metals / Conductors | Semi–conductors | Insulators | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Those solids whose conductivity is very high and resistivity is small | Those solids whose conductivity and resistivity lies between conductors and insulators. | Those solids whose conductivity is very small and resistivity is very high. |
| Conductivity σ = 1/ ρ | σ = 102 to 108 Sm-1 | σ = 105 to 10-6 Sm-1 | σ = 10-11 to 10-19 Sm-1 |
| Resistivity | ρ = 10-2 to 10-8Ωm | ρ = 10-5 to 106 Ωm | ρ = 1011 to 1019 Ωm |
NOTE: Relative values of resistivity are not the only the criteria for distinguishing metals, semiconductors, and insulators from each other. There are also some other criteria like energy gap that distinguish metals, semiconductors, and insulators.
Semiconductor
Semiconductors are those materials whose conductivity and resistivity lies between conductors and insulators.
Types of semiconductors:
- Elemental semiconductors: pure elements like Silicon(Si) and Germanium(Ge).
- Intrinsic Semiconductor
- Extrinsic Semiconductor
- Compound semiconductors:
- Inorganic semiconductors: CdS, GaAs, CdSe, InP etc.
- Organic semiconductors: Anthracine, doped pthalocyanines etc.
- Organic Polymer: polypyrrole, polyaniline, polythiophene, etc.
Important Questions and Answers
What is a semiconductor?
Ans: A semiconductor is a material that has an electrical conductivity between that of a conductor and an insulator. This means that it can conduct electricity, but not as well as a metal, and not as poorly as an insulator.
What are some common semiconductor materials?
Ans: Silicon is the most widely used semiconductor material, but other materials such as germanium, gallium arsenide, and indium phosphide are also used.
Name two factors on which the electrical conductivity of a pure semiconductor at a given temperature depends.
Answer: Two factors on which the electrical conductivity of a pure semiconductor at a given temperature depends,
(i) Energy gap between the conduction band and the valence band.
(ii) Intrinsic charge carrier concentration
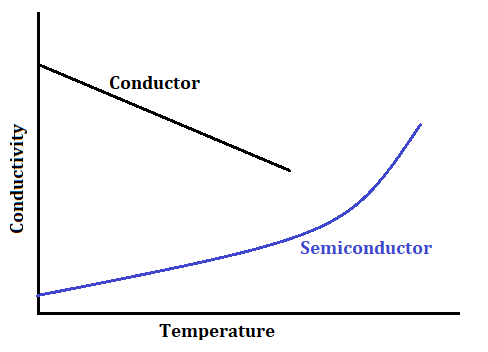
How does the conductivity of a semiconductor change with the rise in temperature?
Answer: The conductivity of a semiconductor increases exponentially with a rise in temperature according to the below relation.

Where, Eg = Energy gap, kb = Boltzman’s constant, T = Absolute temperature
When the temperature of a semiconductor material increases, more electrons jump from the balance band to the conduction band (as the forbidden energy gap is filled by energy supplied by heat) and hence participate in conductivity, so the conductivity of the semiconductor increases.
What is a conductor, and what does its energy band diagram look like?
Answer: A conductor is a material that offers less resistance to the flow of electrical current. Its energy band diagram shows that there is overlap in the valence and conduction bands, meaning that electrons can move freely throughout the material and participate in conductivity.
How does the conductivities of conductor and semiconductor varies with variation in temperature?
Answer:
The conductivity of Conductors decreases with an increase in temperature.
The conductivity of semiconductors increases with an increase in temperature.
मानव संपदा के अंतर्गत समस्त अवकाश संबंधी नियम
👉🖱 What is Electric Flux ? Class 12 Important Topic
👉🖱 Bohrs Atomic Model 12 learn easy
MY YouTube Channel Link : 👉🖱 https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCGpC7nWE0-bBv9I53MM8qjQ
4 basic Conservation Law Additive nature of charge Applications of concept of Accuracy and Precision Applications of Dimensional Analysis Class 5 Maths Combination of Error Conservation of charge Constant Error Detection and measurement of charge: Gold-leaf electroscope Determine the value of the Planck's constant Difference between Accuracy and Precision Ecological Pyramid Electric Charge Electromagnetic Spectrum Electron Emission Electrostatics EM Waves Test Paper Examples of Force in Daily Life Fundamental Forces in Nature Graph between momentum and velocity Hindi grammar Hindi Vyakaran Notes Inertia Instrumental Error Least Count Error Levels of Organization in Ecology limitations of dimensional analysis Measurement of Errors Momentum Nitrogen Fixation Physics Principle of Homogeneity Properties of Electric Charge Quantization of charge quiz Reductionism Relation between Kinetic energy and momentum RO/ARO Hindi Vyakaran Syllabus Systematic Errors Transverse Nature of Electromagnetic Waves Types of Error Unification UP Special GK पर्यावरण और पारिस्थितिकी पर्यावरण के घटक (Components of Environment)
Semiconductor Electronics materials devices and simple circuits, Semiconductor Electronics Class 12, Semiconductor Electronics materials devices and simple circuits, Semiconductor Electronics materials devices and simple circuits, Semiconductor Electronics Class 12, Semiconductor Electronics materials devices and simple circuits, Semiconductor Electronics materials devices and simple circuits, Semiconductor Electronics Class 12
Thank you very much for sharing, I learned a lot from your article. Very cool. Thanks. nimabi
Thank you so much for your response
Thank you very much for sharing, I learned a lot from your article. Very cool. Thanks. nimabi
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
Thank you for your review. Please, mention topic’s name so that I can provide you.
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
Thank you for your review. Yes, ask please
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.