CHARGE:
- Charge is the property of a material due to which an electrostatic force acts between two charge bodies. The SI unit of charge is C (coulomb).
Electrostatic force:
- Electrostatic force is the force acting between two charged body.
Types of charge:
- Charge is of two types (1) Positive charge (2) Negative charge
(1) Positive charge: If a body gives/release electrons, it becomes positively charge.
For ex. Na (neutral) ——–→ Na+ (positively charge)+ 1e–(released electron)
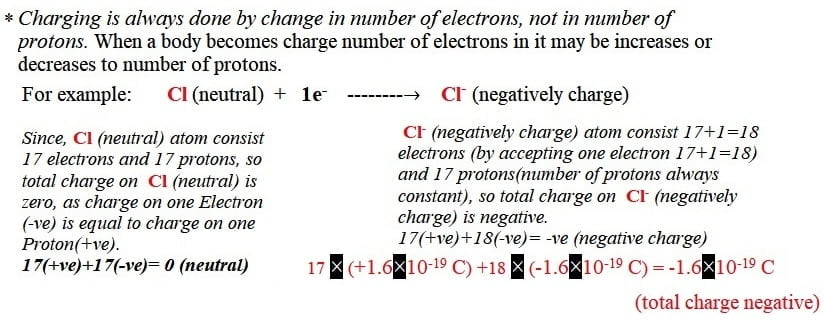
(2) Positive charge: If a body accepts electrons, it becomes negatively charge.
For ex. Cl (neutral) +1e–——–→ Cl– (negatively charge)
- The assignment of positive charge is purely a convention it doesn’t mean that negative charge is less than positive charge i.e. +2C and -2C are same amount of charge. +2C of charge means body acquires this charge by donating/releasing electrons while,-2C of charge means body acquires this charge by accepting electrons.

- All matters surrounding us are made from atoms. Before we study about charge we should know some basic concept of atom.
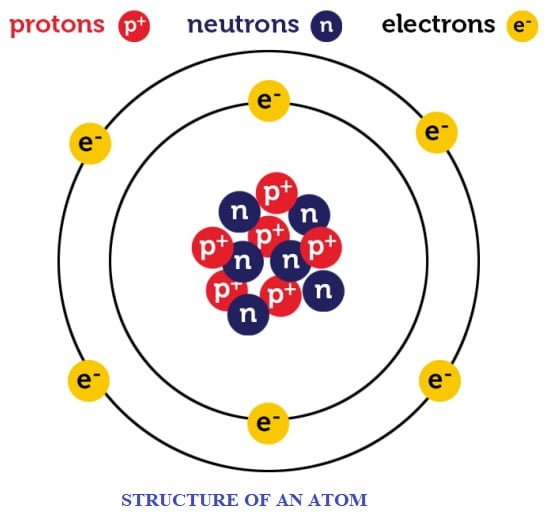
- An atom consists of mainly 3 subatomic particles namely Proton, Electron and Neutron.
- Protons: It is positively charge particle, which lies in nucleus of an atom. Charge on one proton is +1.6*10-19 C.
- Electron: It is negatively charge particle, which revolve surrounding nucleus of an atom. Charge on one electron is -1.6*10-19 C.
- Neutron: It is a neutral (charge less) particle which lies inside nucleus.
- Charge on electrons and protons have equal magnitudes but opposite sign.
Charge on one Electron = – Charge on one Proton
- An atom is always neutral as it contains equal number of electrons and protons. When it becomes Ions number of electron is not equal to number of protons. For example:
K (neutral atom) ——–→ K+ (positive Ion) + 1e– (released electron)
Electric current:
- The rate of flow of electric charge is called electric current. I=Q / t Q= Amount of charge flowing t= time taken
- Current is scalar quantity. It’s SI unit is ampere(A). I=Q / t 1ampere=1coulomb/1second 1A=1C/s
- Definition 1 ampere: The amount of current flowing through a wire is said to be 1 ampere if 1coulomb of charge is flowing through it in 1 second.
- Current is measured by an instrument called Ampere meter(=Ammeter). Ammeter is always connected in series in circuit.