Hello, readers 😊! Here you can learn about Maxwell Equations and Hertz’s experiment. How Hertz produces electromagnetic waves and finds major properties of Electromagnetic Waves.
Maxwell Equations
Maxwell’s Equations
Maxwell’s found that all the basic principles of electromagnetism can be formulated in terms of four fundamental equations called Maxwell’s equation. Maxwell’s equations showed relationship between electric and magnetic field and the relation of electric and magnetic field to the accelerating charge and current. Maxwell’s theory showed that accelerating charge produces electromagnetic wave and the frequency of wave is equal to the frequency of oscillating charge.
(1). Gauss’s Law:
Gauss’s law states that, the total electric flux passing through any closed surface is equal to 1/єo times charge enclosed by the surface. It relates the electric flux through an area with electric charges. Coulomb’s law can be derived from Gauss’s law, hence it can be considered to fundamental equation of electrostatics.

(2). Gauss’s Law in Magnetism:
Gauss’s law in magnetism states that the total magnetic flux, through any closed surface is always equals to zero. It tells that magnetic field lines always forms closed loop and magnetic monopoles does not exist.

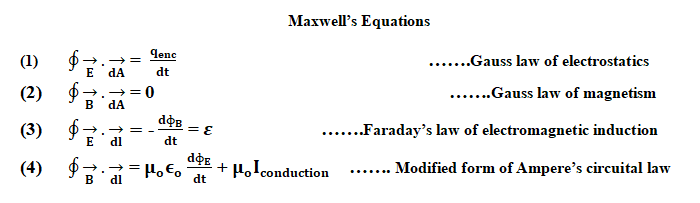
(3). Faraday’s Law of Electromagnetic Induction:
Faraday’s law states that, the magnitude of induced electromotive force in any closed circuit is equal to rate of change of the magnetic flux through the circuit. It tells that changing magnetic flux induces an electric field
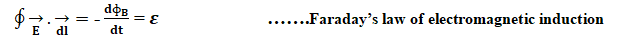
(4). Modified Ampère’s Circuital Law:
The line integral of the magnetic field around any closed circuit is equal to μo times the total current (the sum of conduction and displacement currents) flowing the close circuit.
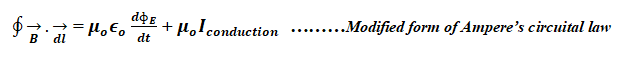
Table of Contents
Hertz’s Experiment
Hertz performed an experiment using an LC circuit and produced electromagnetic waves in a lab in 1887.
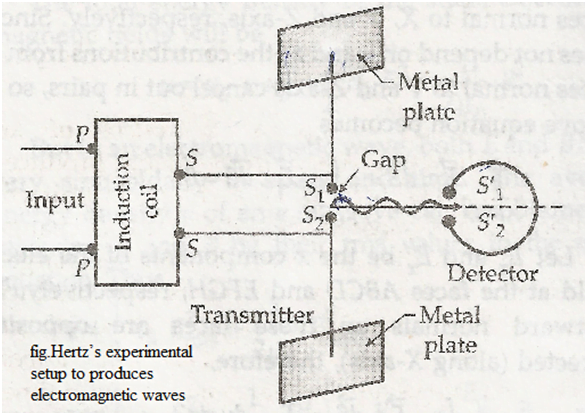
Transmitter consists of capacitor made up of two large square metal plates with sides 60cm x 40cm connected to two highly polished brass sphere (S1, S2) and secondary terminal of induction coil by thick copper wire. A source of high voltage (induction coil) is connected with copper wires, due to it a high potential difference is setup across S1 and S2.this high potential ionizes air in the gap the electrons/ions so produced oscillates back and forth and electromagnetic wave is produced in air gap between two spheres.
Frequency of electromagnetic wave is given by f = 1 / √2πfC
Electromagnetic waves produced here can be detected by Detector. It is a circular wire which both ends have two small polished brass sphere, e.m. waves striking on sphere produces a spark across the air gap.
Hertz demonstrated various properties of electromagnetic wave
- Electromagnetic waves are transverse in nature.
- Electromagnetic radiation has a wave nature.
- Electromagnetic waves travels with speed of light.
Frequency of electromagnetic wave is given by f = 1/ √2πfC
Important Questions from topic
What is the source of electromagnetic wave?
Answer: An oscillating charge or accelerating charge (only by the change in speed) is the source of an electromagnetic wave.
Which of the following, if any, can act as a source of electromagnetic wave?
(i) A charge moving with the constant velocity.
(ii) A charge moving in a circular orbit with changing velocity.
(iii) A charge at rest.
Give reason.
Answer: (i) Because it has zero acceleration, a charge moving at constant velocity cannot produce an electromagnetic wave.
(ii) A charge moving in a circular orbit produces an electromagnetic wave as it has an accelerated motion.
(iii) A charge at rest cannot produce an electromagnetic wave as it has zero acceleration.
How does a charge q oscillating at certain frequency produces electromagnetic waves?
A charge oscillating with frequency f produces an oscillating electric field. An oscillating electric field produces an oscillating magnetic field. An oscillating magnetic field produces an oscillating electric field, and so on. Thus, electromagnetic waves are produced here due to these oscillations, which propagate in a direction perpendicular to the plane of the electric field and magnetic field. The electromagnetic wave produced here has the same frequency as that of the oscillating charge.

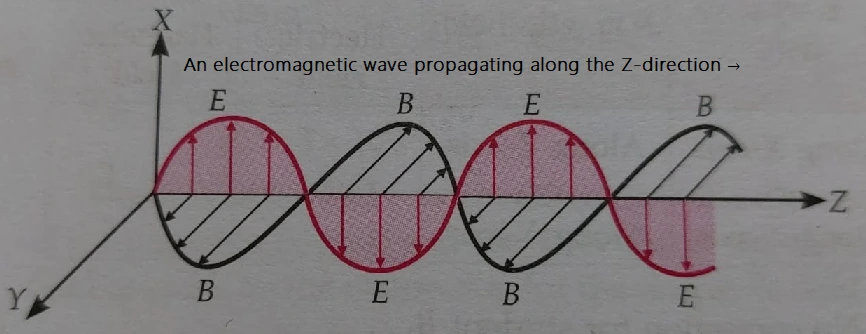
Sketch a schematic diagram depicting electric and magnetic fields for an electromagnetic wave propagating along the Z direction.
Answer: A schematic diagram depicting electric and magnetic fields for an electromagnetic wave propagating along the Z direction.
E = Emax cos(kx-ωt)
B = Bmax cos(kx-ωt)
MY YouTube Channel Link : 👉🖱 https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCGpC7nWE0-bBv9I53MM8qjQ
Maxwell Equations, Maxwell Equations, Maxwell Equations, Maxwell Equations, Maxwell Equations, Maxwell Equations