Chapter-01 Matter in our Surroundings NCERT in-text questions
Matter in our Surroundings NCERT in-text questions page 3
Q. 1: Which of the following are matters?
Chair, air, love, smell, hate, almonds, thought, cold, lemon water, smell of perfume.
Ans: Matters – Chair, air, almonds and lemon water.
While love, smell, hate, thought, cold and smell of perfume are not matters as they don’t have mass and volume.
Concept ☞Anything which have mass and volume is called matter.
Q. 2: Give reasons for the following observation: The smell of hot sizzling food reaches you several metres away, but to get the smell from cold food you have to go close.
Ans: The smell of hot sizzling food reaches you several metres away, but to get the smell of cold food you have to get close because particles (vapour state particles) of hot sizzling food have a high temperature and possess more kinetic energy, which means they diffuse rapidly in the air and reach several metres away, but particles of cold food have a low temperature, hence less kinetic energy and less diffusion.
- Concept ☞ Diffusion is the movement of molecules from higher concentration to lower concentration.
- Particles of matter are continuously moving and moving particle possesses kinetic energy. As the temperature rises, kinetic energy of the particles also increases and particles move faster.
Q. 3: A diver is able to cut through water in a swimming pool. Which property of matter does this observation show?
Ans: A diver is able to cut through water in a swimming pool because there is intermolecular space and intermolecular force between water molecules.
Table of Contents
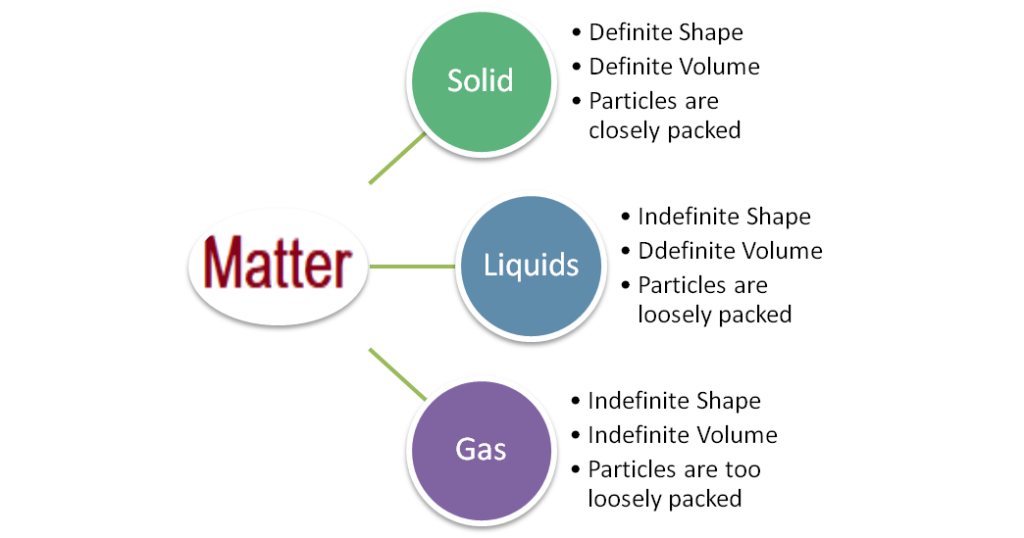
Q. 4: What are the characteristics of the particles of matter?
- Ans: Characteristics of the particles of matter,
- Particles of matter have space between them.
- Particles of matter are continuously moving state.
- The particles of matter are very small – they are small beyond our imagination.
- Particles of matter attract each other.
Matter in our Surroundings NCERT in-text questions page 3
Q. 1: The mass per unit volume of a substance is called density. ( Density = mass/volume). Arrange the following in order of increasing density – air, exhaust from chimneys, honey, water, chalk, cotton and iron.
Ans: Increasing order of density air < exhaust from chimney < cotton < water < honey < chalk < iron.
Q. 2: (a) Tabulate the differences in the characteristics of states of matter. (b) Comment upon the following: rigidity, compressibility, fluidity, filling a gas container, shape, kinetic energy and density.
Ans: (a) The differences in the characteristics of states of matter are given in the following table.
| S.No. | Properties | Solids | Liquids | Gases |
| 1 | shape | definite shape | indefinite shape | indefinite shape |
| 2 | volume | definite volume | definite volume | indefinite volume |
| 3 | density | highly denser | less density | very less density |
| 4 | intermolecular spacing | very small | small | large |
| 5 | intermolecular force | strong | weak | negligible |
| 5 | compressibility | Incompressible | very small | highly compressible |
| 6 | particles movement | Particles of solid cannot move freely | move freely | Gaseous particles are in continuous, random motion |
| 7 | rigidity | rigid | not rigid | not rigid |
| 8 | fluidity | can not flow | can flow | can flow very easily |
(b) (i) Rigidity: The property of a material due to which it does not change its shape and size (opposes deformation) rigidity. Solids are rigid whereas liquids and gases are not.
(ii) Compressibility: The property of material due to which volume of a substance can be decreased by applying pressure on it is called compressibility.
(iii) Fluidity: The property of a material due to which it tends to flow is called fluidity. Gases and liquids are commonly called fluids.
(iv) Filling a gas container: A gas (like CNG, LPG) can be filled in a gas container by compressing it under high pressure and low temperature.
(v) Shape: The property of material due to which it have a definite geometry is called shape.
(vi) Kinetic energy: The energy possessed by an object / molecules due to its motion is called kinetic energy.
(vii) Density: The ratio of mass and volume of a substance is called density.
Q. 3: Give reasons (a) A gas fills completely the vessel in which it is kept.
Ans: (a) A gas fills completely the vessel completely in which it is kept because gaseous molecules are free to move in any direction so gases do not have definite shape, size and acquires the shape, size of container in which gas is kept.
Give reasons (b) A gas exerts pressure on the walls of the container.
Ans: (b) A gas kept in a container exerts pressure on the walls of it because they possess kinetic energy at room temperature and moving randomly inside container. Randomly moving gas molecules collide with container wall applies pressure on it.
Give reasons (c) A wooden table should be called a solid.
Ans: (c) A wooden table should be called a solid because it have all the properties of a solid like definite size and shape, mass, volume, strong intermolecular force between its particles and rigidity.
Give reasons (d) We can easily move our hand in air but to do the same through a solid block of wood we need a karate expert.
Ans: (d) The attraction force between air particles is very weak, which can be break easily with negligible efforts, so we can easily move our hand in the air.
But in case of solids there is strong intermolecular attraction force between its particles which can not break easily and making it difficult to move the hand through it, so we need a karate expert which can apply large efforts.
Q. 4: Liquids generally have lower density as compared to solids. But you must have observed that ice floats on water. Find out why?
Ans: Liquids generally have lower density as compared to solids but Density of ice is less than the density of water that’s why ice floats on water. Density of ice is less than the density of water because ice has crystalline structure in which there is large intermolecular spacing between water molecules as comparison with water in liquid state.
Matter in our Surroundings NCERT in-text questions page 9
Q. 1: Convert the following temperature to Celsius scale: a. 300 K b. 573 K.
Ans: Concept ☞ Temperature in Celsius scale = Temperature in Kelvin scale – 273
a. 300 K Temperature in Celsius scale = 300 – 273 = 27 ℃
b. 573 K Temperature in Celsius scale = 573 – 273 = 300 ℃
Q. 2: What is the physical state of water at: a. 250ºC b. 100ºC?
Ans : (a) The physical state of water at 250°C water is gaseous/vapour state.
(b) At 100°C water coexist in liquid state as well as in gaseous state.
Q. 3: For any substance, why does the temperature remain constant during the change of state?
Ans : When heat is supplied to a substance, it is utilised in two ways. The first part of heat (specific heat) is used to raise the temperature of a substance, while the remaining part of heat (latent heat) is used to change the state of a substance (solid → liquid→ gas) by changing intermolecular force and space. Temperature cannot be changed when a substance changes state because heat is being used to change intermolecular force and space (change in state).
Q. 4: Suggest a method to liquefy atmospheric gases.
Ans: For liquefying atmospheric gases, two methods can be used-
(i) By decreasing the temperature of the gas:- The temperature drop decreases the kinetic energy of the gaseous molecules. As we know, due to kinetic energy, gaseous molecules are in a state of random motion and move away from each other. A decrease in kinetic energy slows/stops such motion due to which intermolecular spacing between gaseous molecules decreases and the gas converts into liquid. As liquids have less intermolecular space between their molecules compared with gases,
(ii) By applying high pressure to the gas:- A very high pressure decreases intermolecular spacing between gaseous molecules and the gas converts into liquid.
Matter in our Surroundings NCERT in-text questions page 10
Q. 1: Why does a desert cooler cool better on a hot dry day?
Ans: On a hot dry day desert cooler cool better because on hot dry day atmosphere is less humid as a result water evaporates easily from by absorbing heat from surrounding produces cooling effect around cooler.
Q. 2: How does the water kept in an earthen pot (matka) become cool during summer?
Ans: An earthen pot (matka) has tiny pores on its wall. A very small amount of water always flows out through these pores and gets evaporated by absorbing heat from surface of matka and making matka and water inside it cool.
Q. 3: Why does our palm feel cold when we put some acetone or petrol or perfume on it?
Ans: Acetone, petrol, and perfume are volatile in nature and evaporate easily by absorbing heat from the palm. Which decreases the temperature of the palm so, our palms feel cold when we put on some acetone or petrol or perfume on them.
Q. 4: Why are we able to sip hot tea or milk faster from a saucer rather than a cup?
Ans: A saucer has a greater surface area than a cup which increases rate of heat loss (cooling) so, tea or milk in a saucer cools down faster in saucer.
Q. 5: What type of clothes should we wear in summer?
Ans: We should always wear white or light-coloured cotton clothes in the summer because light colours reflect heat. Cotton materials have pores, so sweat can be absorbed easily and air passes through pores to cool the body temperature, which makes it comfortable.
Other important topics:
MY YouTube Channel Link : 👉🖱 https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCGpC7nWE0-bBv9I53MM8qjQ
Matter in our Surroundings NCERT in-text questions , Matter in our Surroundings NCERT in-text questions , Matter in our Surroundings NCERT in-text questions , Matter in our Surroundings NCERT in-text questions , Matter in our Surroundings NCERT in-text questions , Matter in our Surroundings NCERT in-text questions , Matter in our Surroundings NCERT in-text questions , Matter in our Surroundings NCERT in-text questions , Matter in our Surroundings NCERT in-text questions , Matter in our Surroundings NCERT in-text questions , Matter in our Surroundings NCERT in-text questions , Matter in our Surroundings NCERT in-text questions