CHAPTER 10 Light Reflection and Refraction NCERT in-text questions
Light Reflection and Refraction NCERT in-text questions page 168
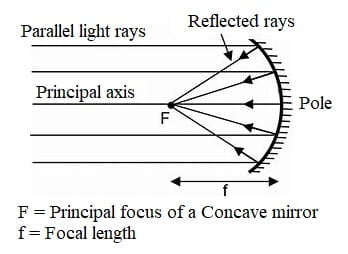
1. Define the principal focus of a concave mirror.
ANSWER: The point on principal axis, at which light rays passing parallel to the principal axis of concave mirror converge after reflection from concave mirror is called principle focus of a concave mirror.
2. The radius of curvature of a spherical mirror is 20 cm. What is its focal length?
ANSWER: Given Radius of curvature (R) of a spherical mirror = 20 cm find f = ?
Formula: Radius of curvature (R) = 2 x Focal length (f)
Focal length (f) = R/2 = 20 cm / 2 =10cm
3. Name a mirror that can give an erect and enlarged image of an object.
ANSWER: Concave mirror can form an erect and enlarged image of an object.
Note: Image formed by concave mirror may be diminished (small), equal in size of object or enlarged.
Image formed by convex mirror is always diminished (small).
Image formed by Plane mirror is always equal in size of object.
4. Why do we prefer a convex mirror as a rear-view mirror in vehicles?
ANSWER: We prefer a convex mirror as a rear-view mirror in vehicles because,
(i) It gives a wider field of view, so driver can to view most of the traffic behind him.
(ii) It always form virtual and erect image.
Table of Contents

Light Reflection and Refraction NCERT in-text questions page 171
1. Find the focal length of a convex mirror whose radius of curvature is 32 cm.
ANSWER: Given: Radius of curvature (R) of a convex mirror = 20 cm find f = ?
Formula: Radius of curvature (R) = 2 x Focal length (f)
Focal length (f) = R/2 = 20 cm / 2 =10cm
2. A concave mirror produces three times magnified (enlarged) real image of an object placed at 10 cm in front of it. Where is the image located?
Light Reflection and Refraction NCERT in-text questions page 176
1. A ray of light travelling in air enters obliquely into water. Does the light ray bend towards the normal or away from the normal? Why?
ANSWER: When a ray of light travelling in air (rarer medium) enters obliquely into water (denser medium), it bends towards the normal due to refraction of light (it happens due to decrease in speed of light). In refraction of light, when light travels from rarer to denser medium it bends towards normal and when light ray travels from denser to rarer medium it bends away from normal.
2. Light enters from air to glass having refractive index 1.50. What is the speed of light in the glass? The speed of light in vacuum is 3 × 108 m/s.
ANSWER: Given: Refractive index of glass = 1.50
Speed of light in medium = speed of light in air /μ
Speed of light in glass = speed of light in air / 1.50 = 3 × 108 m s–1 / 1.55 = 193548387.09 m s–1
3. Find out, from Table 10.3, the medium having highest optical density. Also find the medium with lowest optical density.
ANSWER: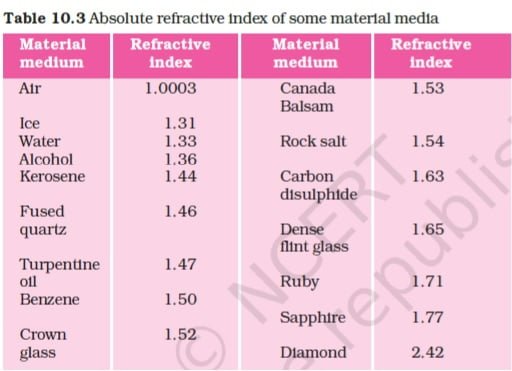
Optical density of a medium = Refractive index of the medium (μ)
Medium having highest optical density is Air ( μ = 1.003)
Medium having lowest optical density is Diamond ( μ = 2.42)
4. You are given kerosene, turpentine and water. In which of these does the light travel fastest? Use the information given in Table 10.3.
ANSWER: Given From table 10.3 Refractive index of kerosene (μ) = 1.44
Refractive index of turpentine oil (μ) =1.47
Refractive index of water (μ) = 1.33
Formula: Refractive index of medium (μ) = Speed of light in air / Speed of light in medium
Speed of light in medium = Speed of light in air /μ = 3 × 108 m s–1 /μ
Speed of light in kerosene = 3 × 108 m s–1 / 1.44 =208333333.33 m/s
Speed of light in turpentine oil = 3 × 108 m s–1 / 1.47 = 204081632.65 m/s
Speed of light in water = 3 × 108 m s–1 / 1.33 = 225563909.77 m/s
So speed of light is more in water.
5. The refractive index of diamond is 2.42. What is the meaning of this statement?
ANSWER: Refractive index of diamond (μ) = 2.42
Speed of light in Diamond = speed of light in air /μ ![]() = speed of light in air / 2.42
= speed of light in air / 2.42
i.e. Speed of light in diamond is 1 / 2.42 times than speed of light in air or light travels 2.42 times slower in diamond as comparison with air.
Light Reflection and Refraction NCERT in-text questions page 184
1. Define 1 dioptre of power of a lens.
ANSWER: Power of lens = 1/ focal length
If focal length of lens is 1m, Power of lens = 1/ 1m = 1m-1= 1D
Power of lens is it said to be one diopter (D) if its focal length is 1 m.
2. A convex lens forms a real and inverted image of a needle at a distance of 50 cm from it. Where is the needle placed in front of the convex lens if the image is equal to the size of the object? Also, find the power of the lens.
3. Find the power of a concave lens of focal length 2 m.
ANSWER: Given: focal length of lens 2 m find power of lens = ?
Power of lens = 1/ focal length = 1 / 2m = 0.5D
MY YouTube Channel Link : 👉🖱 https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCGpC7nWE0-bBv9I53MM8qjQ
Light Reflection and Refraction NCERT in-text questions, Light Reflection and Refraction NCERT in-text questions, Light Reflection and Refraction NCERT in-text questions, Light Reflection and Refraction NCERT in-text questions, Light Reflection and Refraction NCERT in-text questions, Light Reflection and Refraction NCERT in-text questions