CHAPTER 6 Life Processes NCERT Questions Solution
1. The kidneys in human beings are a part of the system for
(a) nutrition. (c) excretion.
(b) respiration. (d) transportation.
Answer: (c) excretion.
2. The xylem in plants are responsible for
(a) transport of water. (c) transport of amino acids.
(b) transport of food. (d) transport of oxygen.
Answer: (a) transport of water.
3. The autotrophic mode of nutrition requires
(a) carbon dioxide and water. (c) sunlight.
(b) chlorophyll. (d) all of the above.
Answer: (d) all of the above.
4. The breakdown of pyruvate to give carbon dioxide, water and energy takes place in
(a) cytoplasm. (c) chloroplast.
(b) mitochondria. (d) nucleus.
Answer: (b) mitochondria. This process is known as the citric acid cycle (also called the Krebs cycle or TCA cycle), and it is a crucial part of cellular respiration, where glucose is broken down to produce energy in the form of ATP.
Table of Contents

5. How are fats digested in our bodies? Where does this process take place?
Answer : Fats are present in the form of large globules in the small intestine. The small intestine gets the secretions in the form of bile juice and pancreatic juice respectively from the liver and the pancreas. The bile salts (from the liver) break down the large fat globules into smaller globules so that the pancreatic enzymes can easily act on them. This is referred to as emulsification of fats. It takes place in the small intestine.
6. What is the role of saliva in the digestion of food?
Answer: Saliva, produced by salivary glands, helps in food digestion. It is mixed with churned food in the mouth and moistens food, making it easier to swallow and move down the esophagus. Saliva contains an amylase enzyme that starts breaking down starches into sugars. This enzyme initiates the digestion process in the mouth. Saliva also enhances taste perception, maintains a mouth-friendly pH, and contains antibacterial agents for oral health.
7. What are the necessary conditions for autotrophic nutrition and what are its by products?
Answer: In autotrophic nutrition, food is made by the process of photosynthesis. Photosynthesis is done in autotrophs with the intake of water, carbon dioxide, and chlorophyll pigment in the presence of sunlight. Oxygen and carbohydrates are the by-products.

8. What are the differences between aerobic and anaerobic respiration? Name some organisms that use the anaerobic mode of respiration.
Answer: Differences between aerobic and anaerobic respiration –
| Aerobic respiration | Anaerobic respiration | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | It occurs in presence of oxygen. | It occurs in absence of oxygen. |
| 2 | It involves the exchange of gases between organism and outside environment. | No exchange of gases. |
| 3 | It occurs in cytoplasm and mitochondria. | It occurs in cytoplasm. |
| 4 | Carbon dioxide and water is released. | End product may vary. |
| 5 | It yields 36 ATPs. | It yields 2 ATPs. |
Anaerobic respiration occurs in yeast, animal muscles and roots of some water logged plants.
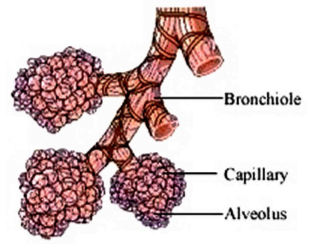
9. How are the alveoli designed to maximise the exchange of gases?
Answer: Lungs consist of small balloon-like structures called alveoli. The walls of the alveoli consist of an extensive network of blood vessels. Both lungs contain approximately 700 million lungs. The alveolar surface, when spread out, covers about 80 m2 area. This large surface area makes the gaseous exchange more efficient.
10. What would be the consequences of a deficiency of haemoglobin in our bodies?
Answer: Haemoglobin helps in cellular respiration by transporting oxygen to cells. So the deficiency of haemoglobin causes less availability of oxygen, thus making it difficult for animals to breathe and feeling tired. The deficiency of haemoglobin in our bodies is called anemia.
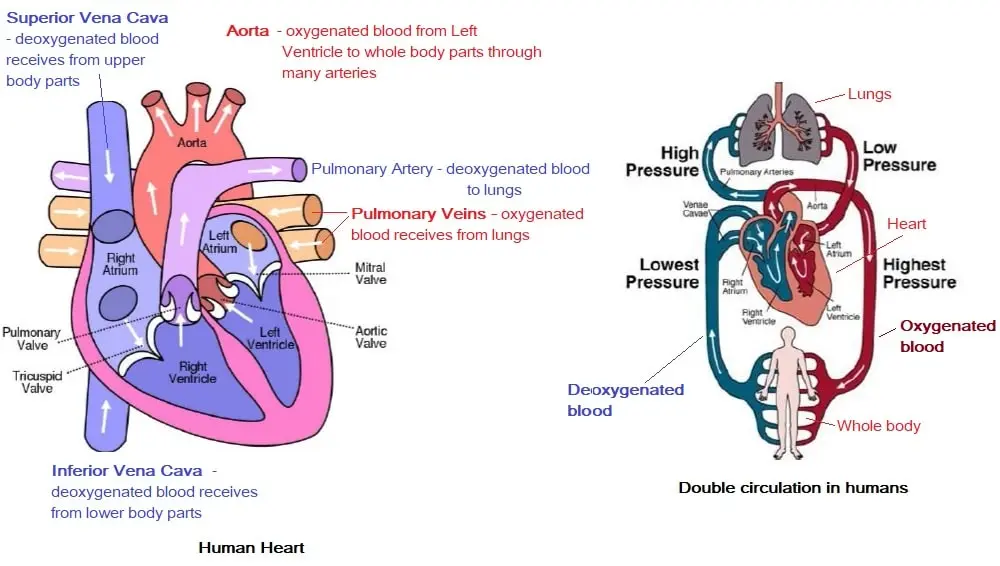
11. Describe double circulation of blood in human beings. Why is it necessary?
Answer: Human heart have four chamber (i) right atrium (ii) right ventricle (iii) left atrium (iv) left ventricle
The heart has superior and inferior vena cava, which carries de-oxygenated blood from the upper and lower regions of the body respectively and supplies this deoxygenated blood to the right atrium of the heart.
The right atrium then contracts and passes the de-oxygenated blood to the right ventricle, through an auriculo-ventricular aperture.
Then the right ventricle contracts and passes the de-oxygenated blood into the two pulmonary arteries, which pumps it to the lungs where the blood becomes oxygenated. From the lungs, the pulmonary veins transport the oxygenated blood to the left atrium of the heart.
Then the left atrium contracts and through the auriculo-ventricular aperture, the oxygenated blood enters the left ventricle.
The blood passes to aorta from the left ventricle. The aorta gives rise to many arteries that distribute the oxygenated blood to all the regions of the body.
Therefore the blood goes twice through the heart. this is known as double circulation.
Importance of double circulation:
The separation of oxygenated and de-oxygenated blood allows a more efficient supply of oxygen to the body cells. This efficient system of oxygen supply is very useful in warmblooded animals such as human beings.
As we know, warm-blooded animals have to maintain a constant body temperature by cooling themselves when they are in a hotter environment and by warming their bodies when they are in a cooler environment. Hence, they require more O2 for more respiration so that they can produce more energy to maintain their body temperature. Thus, the circulatory system of humans is more efficient because of the double circulatory heart.
12. What are the differences between the transport of materials in xylem and phloem?
Answer: Differences between the transport of materials in xylem and phloem
| Transport of materials in xylem | Transport of materials in phloem |
|---|---|
| Xylem is responsible for transporting water and minerals from roots to other parts of the plant. | Phloem transports organic compounds, mainly sugars (like glucose), produced in photosynthesis, from leaves to various plant tissues. |
| This movement occurs through capillary action and cohesion, primarily driven by transpiration. | phloem transports organic compounds, mainly sugars (like glucose), produced in photosynthesis, from leaves to various plant tissues. |
| Xylem operates unidirectionally. | Phloem transport can be bidirectional. |
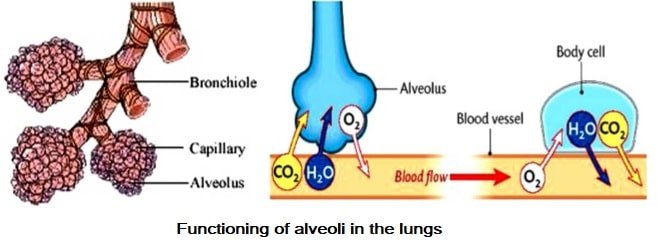
13. Compare the functioning of alveoli in the lungs and nephrons in the kidneys with respect to their structure and functioning.
Structure of alveoli:
(i) Alveoli are tiny balloon like structures present inside the lungs.
(ii) The walls of the alveoli are one cell thick and it contains an extensive network of blood capillaries.
Function of alveoli:
(i) The exchange of Oxygen and carbon dioxide takes place between the blood of the capillaries that surround the alveoli and the gases present in the alveoli.
(ii) Alveoli are the site of gaseous exchange.
Structure of nephrons:
(i) Nephrons are tubular structures present inside the kidneys.
(ii) Nephrons are made of glomerulus, bowman’s capsule, and a long renal tube. It also contains a cluster of thin-walled capillaries.
Function of nephrons:
(i)The blood enters the kidneys through the renal artery which branches into many capillaries in the glomerulus. The water and solute are transferred to the nephron at Bowman’s capsule. Then the filtrate moves through the proximal tubule and then down into the loop of henle. From henle’s loop, filtrate passes into the distal tubule and then to the collecting duct. The collecting duct collects the urine from many nephrons and passes it to the ureter. During the flow of filtrate, some substances such as glucose, amino acids, and water are selectively reabsorbed.
(ii) Nephrons are basic functional unit of kidney (filtration).
MY YouTube Channel Link : 👉🖱 https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCGpC7nWE0-bBv9I53MM8qjQ
Life Processes NCERT Questions Solution, Life Processes NCERT Questions Solution, Life Processes NCERT Questions Solution, Life Processes NCERT Questions Solution, Life Processes NCERT Questions Solution, Life Processes NCERT Questions Solution, Life Processes NCERT Questions Solution, Life Processes NCERT Questions Solution, Life Processes NCERT Questions Solution
Life Processes NCERT Questions Solution, Life Processes NCERT Questions Solution, Life Processes NCERT Questions Solution, Life Processes NCERT Questions Solution, Life Processes NCERT Questions Solution, Life Processes NCERT Questions Solution
I have read some excellent stuff here Definitely value bookmarking for revisiting I wonder how much effort you put to make the sort of excellent informative website.