CHAPTER 06 Life Processes NCERT in-text questions
Life Processes NCERT in-text questions page 95
1. Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi cellular organisms like humans?
Answer: Multi cellular organisms like humans have complex body system so their energy demand is high and quick which is fulfilled by respiration in presence of oxygen. Since diffusion is slow process so it can not supply sufficient amount of oxygen for required of multi cellular organisms like humans.
2. What criteria do we use to decide whether something is alive?
Answer: If something is alive, it should reproduce, grow, show movement, locomotion, metabolism, and have a well-defined body structure.
3. What are outside raw materials used for by an organism?
Answer: Outside raw materials used by an organism are,
(i) Food for fulfill their energy needs keep them healthy.
(ii) Water for food preparation, transportation of food, digestion and body temperature regulation.
(iii) Oxygen for respiration.
(iv) Sunlight for photosynthesis by plants.
4. What processes would you consider essential for maintaining life?
Answer: The essential processes for maintaining life include metabolism, growth, reproduction, response to stimuli, and homeostasis. These processes collectively allow organisms to function, adapt, and survive in their environments.
Table of Contents

Life Processes NCERT in-text questions page 101
1. What are the differences between autotrophic nutrition and heterotrophic nutrition?
Answer: Differences between autotrophic nutrition and heterotrophic nutrition-
| Autotrophic Nutrition | Heterotrophic Nutrition |
|---|---|
| Here, organisms can synthesise their own food through photosynthesis or chemosynthesis. | These organisms cannot synthesise their own food, but they are dependent on autotrophs for their food. |
| These organisms use inorganic materials like CO2, water and, in the presence of sunlight, perform photosynthesis to convert them to organic materials (making their own food). | These organisms obtain their food from organic materials and convert them into simpler ones through processes like digestion and cellular respiration. |
| All plants, algae, and some bacteria are autotrophs. | All animals, fungi, and most of the bacteria are Heterotrophs. |
2. Where do plants get each of the raw materials required for photosynthesis?
Answer: Plants obtain the raw materials required for photosynthesis from various sources:
- Carbon Dioxide (CO2): Plants obtain carbon dioxide from the surrounding air through small pores called stomata.
- Water (H2O): Plants absorb water from the soil through their roots. which is transported to leaves through xylem. Sunlight: Plants capture sunlight using chlorophyll pigment found in chloroplasts.
- Mineral Nutrients: Plants absorb essential mineral nutrients, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, from the soil through their roots.
3. What is the role of the acid in our stomach?
Answer: The acid in our stomach, serves a crucial role in the digestive process,
- Protein Digestion: Stomach acid helps to denature proteins (break into smaller peptides), making their digestion easier.
- Activation of Enzymes: The low pH of stomach acid activates some enzyme.
- Killing Microorganisms: Stomach acid’s acidic environment helps kill microorganisms present in ingested food.
4. What is the function of digestive enzymes?
Answer: Digestive enzymes help in the digestion of food by breaking down complex food molecules into smaller, simpler molecules that the body can absorb and use for energy, growth, and repair. Each type of enzyme targets a specific type of food component:

5. How is the small intestine designed to absorb digested food?
Answer: The small intestine is designed in such a way that it can help in digestion and absorb nutrients. It has finger-like villi/microvilli, which increase effective surface area. Capillaries and lacteals in villi absorb nutrients, while selective transport mechanisms ensure efficient uptake of glucose, amino acids, and fats. Goblet cells secrete mucus to protect the internal layer of the intestine. The intestine’s pH is regulated for optimal enzyme activity.
Life Processes NCERT in-text questions page 105
1. What advantage over an aquatic organism does a terrestrial organism have with regard to obtaining oxygen for respiration?
Answer: Terrestrial organisms have an advantage over aquatic ones in getting oxygen easily for breathing, as terrestrial organisms can take oxygen with the help of their lungs directly from the air, which contains a higher concentration of oxygen, while aquatic organisms use dissolved oxygen from water, which is at a lower concentration. So terrestrial organisms have a faster metabolism compared to aquatic organisms, which need to work harder to extract oxygen from water.
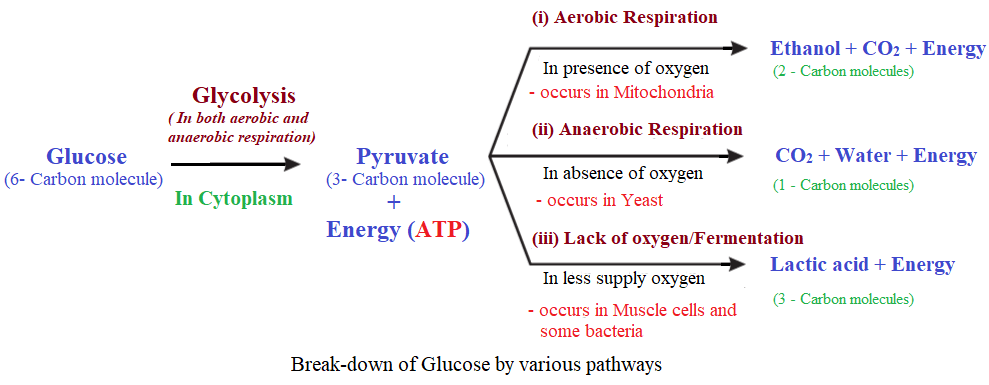
2. What are the different ways in which glucose is oxidised to provide energy in various organisms?
Answer: Glucose is the main source of energy in various organisms. It undergoes oxidation through different pathways to produce energy, mainly in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In the cytoplasm of various organisms, glucose is broken down into two molecules of pyruvate. There are mainly three pathways in which pyruvate is further oxidised to simpler molecules and produces energy in the form of ATP.
- Aerobic Respiration – Highly energy efficient
- Anaerobic Respiration – Less energy efficient than aerobic respiration
- Lack of oxygen/fermentation – less energy efficient but allow survival when oxygen is scarce. Lactic acid is formed in muscle during physical exercise due to less availability of oxygen.
3. How is oxygen and carbon dioxide transported in human beings?
Answer: Oxygen and carbon dioxide are transported in humans through two main systems: the respiratory system and the circulatory system.
- Oxygen Transport: Oxygen is inhaled through the respiratory system, enters the lungs, and diffuses across the alveoli (tiny air sacs) into the bloodstream. Oxygen molecules attach to hemoglobin, forming oxyhemoglobin. This oxyhemoglobin is carried by RBCs throughout the body’s cells, where it releases oxygen for energy production through aerobic respiration.
- Carbon Dioxide Transport: Carbon dioxide, a waste product, is generated by cells during metabolism and diffuses into the bloodstream, where it forms bicarbonate ions (HCO₃⁻) in the plasma. Bicarbonate ions are transported to the lungs through the bloodstream. In the lungs, the process is reversed, and carbon dioxide is exhaled.
4. How are the lungs designed in human beings to maximise the area for exchange of gases?
Answer: The lungs in humans are designed to enhance gaseous exchange. Within the lungs, the air passage divides into smaller and smaller tubes called bronchi, which in turn form bronchioles. The bronchioles terminate in balloon-like structures called alveoli. The alveoli present in the lungs maximise the surface area for the exchange of gases. The alveoli have thin walls and contain an extensive network of blood vessels to facilitate the exchange of gases. This ensures body tissues receive oxygen and waste carbon dioxide is removed effectively.
Life Processes NCERT in-text questions page 109
1. What are the components of the transport system in human beings? What are the functions of these components?
2. Why is it necessary to separate oxygenated and deoxygenated blood in mammals and birds?
3. What are the components of the transport system in highly organised plants?
4. How are water and minerals transported in plants?
5. How is food transported in plants?
Life Processes NCERT in-text questions page 112
1. Describe the structure and functioning of nephrons.
2. What are the methods used by plants to get rid of excretory products?
3. How is the amount of urine produced regulated?
MY YouTube Channel Link : 👉🖱 https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCGpC7nWE0-bBv9I53MM8qjQ
Life Processes NCERT in-text questions, Life Processes NCERT in-text questions, Life Processes NCERT in-text questions, Life Processes NCERT in-text questions, Life Processes NCERT in-text questions, Life Processes NCERT in-text questions, Life Processes NCERT in-text questions, Life Processes NCERT in-text questions, Life Processes NCERT in-text questions, Life Processes NCERT in-text questions