Learn electric dipole at easy class 12
Electric dipole :
A pair of equal and opposite electrical charges separated by a small distance is known as electric dipole.
The net charge on an electric dipole is zero as it constitutes a pair of equal and opposite charges.
Electric dipoles are important in many areas of physics, including electrostatics, electromagnetism, and quantum mechanics. They play a significant role in the behavior of molecules in chemistry, and in the interactions between charged particles in materials science and engineering. The electric dipole moment is also used as a measure of the polarity of a molecule or material.
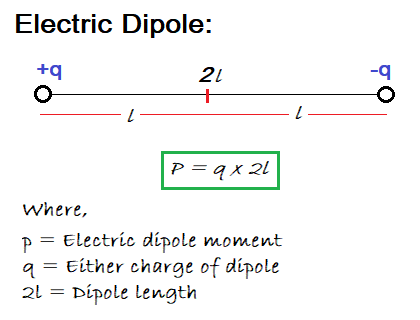
Table of Contents
Electric dipole moment:
The strength of an electric dipole is measured in terms of its electric dipole moment.
The electric dipole moment is the product of the magnitude of either charges and separation between them.
Mathematically, the electric dipole moment is given by the formula:
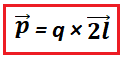
p = q × 2l
Where, q is the magnitude of the charge, and 2l is the distance between the charges.
The electric dipole moment is a vector quantity, which means that it has both magnitude and direction. The direction of the electric dipole moment is defined as pointing from the negative charge to the positive charge.
Electric dipole moments are important in many areas of physics, including electromagnetism, quantum mechanics, and molecular physics. They are used to describe the behavior of atoms, molecules, and other charged particles in electric fields.
Unit of electric dipole moment:
The SI unit of electric dipole moment is coulomb-meter (C⋅m). In practice, the dipole moment is often expressed in Debye units (D), where 1 D = 3.336 × 10-30 C⋅m.
Ideal electric dipole:
An electric dipole is said to be ideal if the magnitude of either charge is large and the separation between both charges is infinitesimal.
In other words, an ideal electric dipole is a pair of point charges of opposite sign that are very close to each other, with the distance between them being much smaller than any other distance of interest.

Electric field due to an Electric Dipole at a point on axial line:
To derive an expression for the electric field intensity at an axial point due to an electric dipole, we can consider an electric dipole consists of two charges, +q and -q, separated by a distance 2l. From the midpoint of the dipole O, at a distance r there is an observation point P on axis of the dipole, where we have to find out electric field intensity.
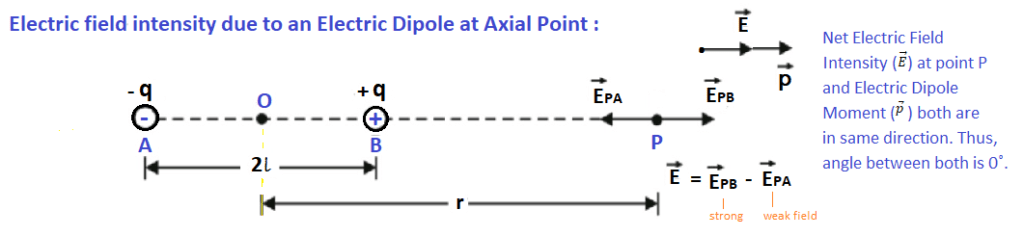
Key Concept: The electric field intensity (E) at the axial point can be determined by summing the individual electric fields created by the two charges of the dipole. Since the charges are equal in magnitude and opposite in sign, the electric fields created by them will have the same magnitude but point in opposite directions.
The electric field intensity (EPA) at point P due to charge A (+q), can be calculated using Coulomb’s law is given by:
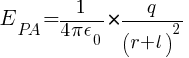
Similarly, The electric field intensity (EPB) at point P due to charge B (-q), can be calculated using Coulomb’s law is given by :
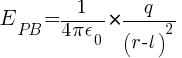
To find the total electric field intensity at the axial point, we Vector sum the individual electric field intensities due to both charges:
Eaxial = E = EPB – EPA
Substituting the expressions for EPB and EPA, we have:
Eaxial = E = 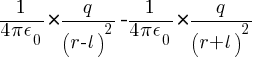
Eaxial = E = ![{q/{4 pi epsilon_0} } * [{1 / ( r - l )^2} - { 1 / ( r + l )^2}] {q/{4 pi epsilon_0} } * [{1 / ( r - l )^2} - { 1 / ( r + l )^2}]](https://mywebpathshala.com/wp-content/plugins/wpmathpub/phpmathpublisher/img/math_966.5_a5266a1000d99f8a18ab901b210e7c60.png)
Eaxial = E = 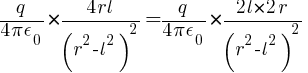
putting value 2ql = p (Dipole moment)
Eaxial = E = 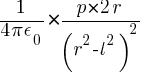
Eaxial = E = 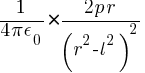
If dipole is short, when r >> l
Eaxial = E = 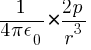
In vector form,
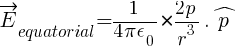
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) from Electric Dipole
Q1: What is an electric dipole?
Answer: An electric dipole is a pair of equal and opposite charges separated by a small distance.
Q2: What is an axial point?
Answer: An axial point is a point located along the axis of an electric dipole.
Q3: What is the importance of studying electric field intensity due to dipole?
Answer: Studying electric field due to electric dipole is important because it helps us understanding the behavior of electric dipoles and their interactions with other charges or dipoles.
Q4: How can we calculate the electric field intensity at an axial point?
Answer: The electric field intensity at an axial point can be calculated by summing the electric fields produced by the positive and negative charges of the dipole using Coulomb’s law. The expression for the electric field intensity is:
Eaxial = E = 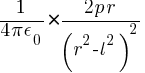
Q5: What factors affect the electric field intensity due to electric dipole at an axial point?
Answer: The electric field intensity at an axial point is influenced by (i) Electric dipole moment (ii) distance of observation point from the mid point of electric dipole (r).
Q6: How does the electric field intensity vary as we move along the axis of the dipole?
Answer: The electric field intensity decreases as we move away from the dipole along its axis.
Q7: Can the electric field at an axial point be zero?
Answer: (i) When the point is at an infinite distance from the dipole: As we move to an infinite distance from the electric dipole, the electric field becomes weaker. Eventually, at infinitely far distance, the electric field tends to zero. (ii) when r = l then also E = 0.
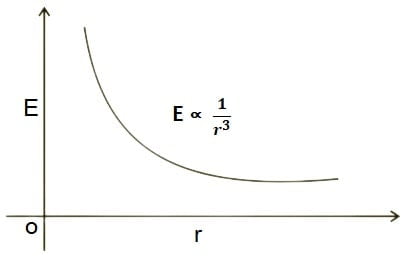
At what point is the electric field at its maximum due to the electric dipole?
Answer: As we move away from the dipole along the axial line, the electric field strength decreases with increasing distance. The magnitude of the electric field decreases inversely proportional to the cube of the distance from the dipole.
Therefore, if you are looking for the point where the electric field due to an electric dipole is maximum, you would need to consider any point along the axial line between the charges of the dipole i.e. at center of electric dipole.
Q8: What are the practical applications of understanding the electric field intensity at an axial point?
Answer: Understanding the electric field intensity at an axial point is crucial in various fields, including physics, electrical engineering, and molecular biology. It helps in analysing the behaviour of molecules, designing electrical circuits, and studying electromagnetic interactions.
What is an electric dipole?
Ans: An electric dipole is a pair of electric charges of equal magnitude but opposite sign, separated by a distance.
What is the electric dipole moment?
Ans: The electric dipole moment is a measure of the separation between positive and negative charges in an electric dipole. It is defined as the product of the magnitude of the charges and the distance between them.
What is the net charge on electric dipole?
Ans: The net charge on an electric table is zero as it constitutes a pair of equal and opposite charges.
What is the SI unit of electric dipole moment?
Ans: The SI unit of electric dipole moment is coulomb-meter (C⋅m).
What is a Debye?
Ans: A Debye is a unit used to express electric dipole moments. One Debye is equal to 3.336 × 10-30 C⋅m.
What are some applications of electric dipoles?
Ans: Electric dipoles are important in many areas of physics and engineering, including electromagnetism, molecular physics, material science, and biophysics. They are used to understand the behavior of electric fields, describe the distribution of charge within molecules, and measure the electrical activity of biological systems.
How does an external electric field interact with an electric dipole?
Ans: An external electric field can exert a torque on an electric dipole, causing it to align itself with the field. This phenomenon is known as electric dipole moment alignment or polarization.
What is the difference between an electric dipole and a magnetic dipole?
Ans: An electric dipole consists of a pair of electric charges separated by a distance, while a magnetic dipole consists of a current loop or a magnetized object. Electric dipoles interact with electric fields, while magnetic dipoles interact with magnetic fields.
Can an electric dipole be formed by a single charged particle?
Ans: No, an electric dipole requires a pair of electric charges of opposite sign. A single charged particle can create an electric field, but not an electric dipole.
electric dipole class 12 , Learn electric dipole at easy class 12 , Learn electric dipole at easy class 12 , Learn electric dipole at easy class 12 , Learn electric dipole at easy class 12 , Learn electric dipole at easy class 12, Learn electric dipole at easy class 12 , Learn electric dipole at easy class 12, Learn electric dipole at easy class 12 , Learn electric dipole at easy class 12,
Learn electric dipole at easy class 12 , Learn electric dipole at easy class 12, Learn electric dipole at easy class 12 , Learn electric dipole at easy class 12, Learn electric dipole at easy class 12 , Learn electric dipole at easy class 12, Learn electric dipole at easy class 12 , Learn electric dipole at easy class 12
MY YouTube Channel Link 👉🖱 : https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCGpC7nWE0-bBv9I53MM8qjQ