Chapter-02 Is matter around us pure?
Is matter around us pure NCERT in-text questions
NCERT in-text questions page 15
Q. 1: What is meant by a substance?
Ans: A substance is a pure single form of matter.
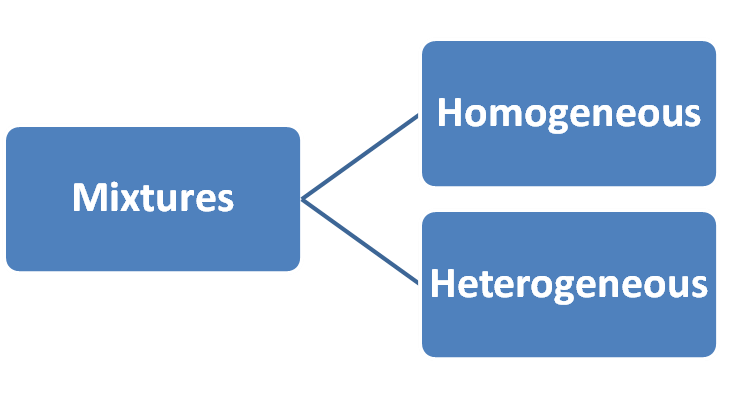
Q. 2: List the points of differences between homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures.
Answer:
| Homogeneous Mixtures | Heterogeneous Mixtures |
| Mixtures having uniform composition throughout is called Homogeneous mixture. | Mixture having non-uniform compositions throughout is called Heterogeneous mixture. |
| Component of mixture are not visible (can not be seen easily) | Component of mixture are visible. |
| Components of mixture can not be separated easily. | Components of mixture can be separated easily. |
| It consists of a single phase. | It consists of a two or multiple phase. |
| Example:(i) Mixtures of Sugar and Water (ii) Mixtures of sodium chloride and water (iii) blood (iv) air | Example: Mixtures of (i) Salt and Sand (ii) sodium chloride and iron filings (iii) salt and sulphur (iv) oil and water |
Table of Contents
NCERT in-text questions page 18
Q. 1: Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures with examples.
Answer: see solution of above question.
Q. 2: How are sol, solution and suspension different from each other?
Answer:
| Sol (colloid solution) | Solution | Suspension |
| It is a heterogeneous mixture. | It is a homogeneous mixture. | It is a heterogeneous mixture. |
| The particles size is moderate (neither too small not large). | The particles of a solution are smaller than 1 nm (10-9 metre) in diameter. So, they cannot be seen by naked eyes. | The particles of a suspension can be seen by the naked eye. |
| Tyndall effect is observed. | Because of very small particle size, they do not scatter a beam of light passing through the solution. So, the path of light is not visible in a solution i.e. does not shows Tyndall effect. | The particles of a suspension scatter a beam of light passing through it and make its path visible. usually Tyndall effect is observed. |
| Quiet stable | The solute particles do not settle down when left undisturbed, that is, a solution is stable. The solute particles cannot be separated from the mixture by the process of filtration. | The solute particles settle down when a suspension is left undisturbed, that is, a suspension is unstable. They can be separated from the mixture by the process of filtration. When the particles settle down, the suspension breaks and it does not scatter light any more. |
Q. 3: To make a saturated solution, 36 g of sodium chloride is dissolved in 100 g of water at 293 K. Find its concentration at this temperature.
Answer: Mass of solute (sodium chloride) = 36g
Mass of solvent (water) = 100g
Mass of solution = Mass of (solute + solvent) = 36g + 100g = 136g
Concentration of saturated solution = (Mass of solute /Mass of solution ) × 100%
= (36/136) × 100% = 26.471%
| Key Concept ☞ Solution: A solution is a homogeneous mixture of two or more substances. Solvent: The component of the solution that dissolves the other component in it (usually the component present in larger amount) is called the solvent. Solute: The component of the solution that is dissolved in the solvent (usually present in lesser quantity) is called the solute. |
NCERT in-text questions page 24
Q. 1: How will you separate a mixture containing kerosene and petrol (difference in their boiling points is more than 25ºC), which are miscible with each other?
Answer: A mixture containing kerosene and petrol (difference in their boiling points is more than 25ºC), which are miscible with each other can be separated by distillation process.
Key Concept ☞ Distillation: Distillation is the process in which two miscible liquids can be separated on the basis of their boiling point. Both liquids should boil without decomposition and have a sufficient difference in their boiling points. A mixture of miscible liquids is boiled in a closed container. Both liquids boil/vaporized at different temperatures and also condense differently at different temperatures, hence getting separated.
Q. 2: Name the technique to separate (i) butter from curd, (ii) salt from sea-water, (iii) camphor from salt.
Answer:
| S. No. | Material | Separation technique |
| 1 | butter from curd | centrifugation |
| 2 | salt from sea-water | crystallization/vaporization |
| 3 | camphor from salt | sublimation (camphor is sublimable but salt is not) |
Q. 3: What type of mixtures are separated by the technique of crystallisation?
Answer: Solid crystals from impure solution are separated by crystallization.
Key Concept ☞ Crystallisation: Crystallisation is a process that separates a pure solid in the form of its crystals from a solution. It is a solid-liquid separation technique.
NCERT in-text questions page 24
Q. 1: Classify the following as chemical or physical changes:
| cutting of trees | physical changes |
| melting of butter in a pan | physical changes |
| rusting of almirah | chemical changes |
| boiling of water to form steam | physical changes |
| passing of electric current, through water and the water breaking down into hydrogen and oxygen gases | chemical changes |
| dissolving common salt in water | chemical changes |
| making a fruit salad with raw fruits | physical changes |
| burning of paper and wood | chemical changes |
| Key Concept ☞ Physical change: If only physical properties (like shape, size, color, hardness, rigidity, fluidity, density, melting point, boiling point and state of substance ) change, the substance is said to be changing physically. Chemical change: If only chemical properties (like the formation or breaking of new bonds) change, the substance is said to be changing chemically. A new substance with different properties is formed in chemical change. |
Q. 2: Try segregating the things around you as pure substances or mixtures.
Pure substances: water, iron, pencil lead, sugar.
Mixtures: Air, blood, soil, milk, steel, paper
Key Concept ☞ Pure substance: Pure substances are substances that are made up of only one kind of particles/matter.
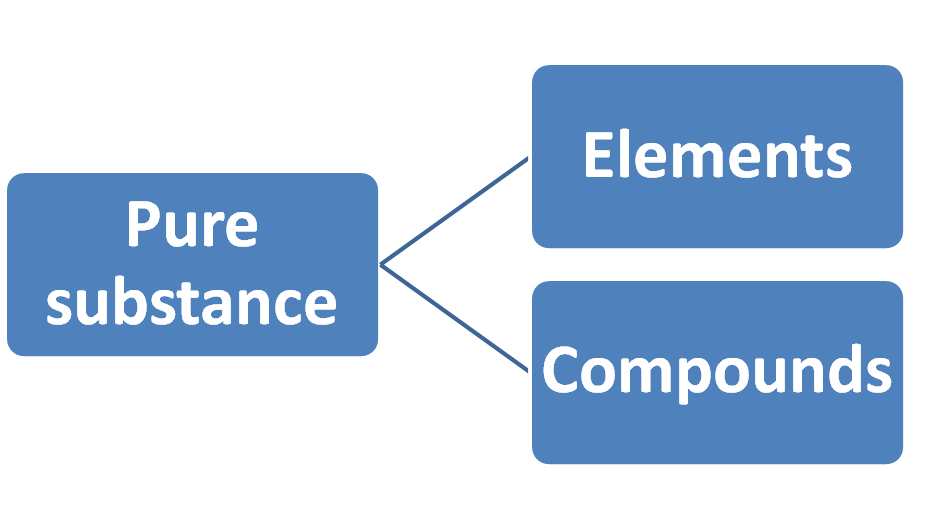
Key Concept ☞ Mixture: In chemistry, when two or more substances mix with each other called mixture. A mixture shows the properties of the constituent substances.
MY YouTube Channel Link : 👉🖱 https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCGpC7nWE0-bBv9I53MM8qjQ
Is matter around us pure NCERT in-text questions , Is matter around us pure NCERT in-text questions , Is matter around us pure NCERT in-text questions , Is matter around us pure NCERT in-text questions , Is matter around us pure NCERT in-text questions , Is matter around us pure NCERT in-text questions , Is matter around us pure NCERT in-text questions , Is matter around us pure NCERT in-text questions , Is matter around us pure NCERT in-text questions , Is matter around us pure NCERT in-text questions , Is matter around us pure NCERT in-text questions , Is matter around us pure NCERT in-text questions