Forward and reverse bias I-V characteristics of a pn-junction diode
Forward and reverse bias I-V characteristics of a pn-junction diode
A graph plotted between voltage across pn-junction and current flowing through it is called I-V Characteristic.
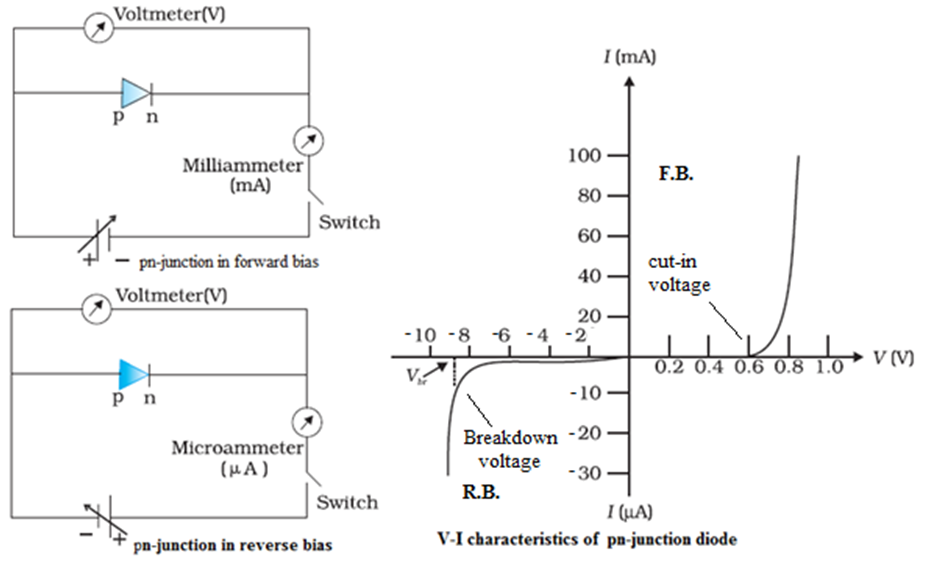
Forward Characteristic:
- V-I graph is not straight line i.e. Ohm’s law is not obeyed.
- Resistance across junction is low.
- Up to cut-in voltage/knee voltage (0.7V for Si and 0.2V for Ge diode) current increases negligibly with increase in voltage.
- After cut-in voltage, current increases exponentially with increase in voltage.
Reverse Characteristic:
- VI-graph is not straight line.
- Resistance across junction is high.
- Initially a very small current is obtained called Reverse saturation current (Leakage current), which is almost independent on applied voltage. Reverse saturation current is due to minority charge carrier and is dependent on doping concentration, diffusion length and device temperature.
- At Breakdown-voltage/Peak inverse voltage current increases suddenly to a large value.