Force and Laws of Motion
Hello, readers ! Here on this webpage you can learn important concepts of chapter-09 ‘Force and Laws of Motion’ and can get class notes, NCERT question solutions, NCERT in-text question solutions, other important question-answers and can participate in quizzes. Force and Laws of Motion.
Table of Contents
Force and Laws of Motion – INDEX
Force
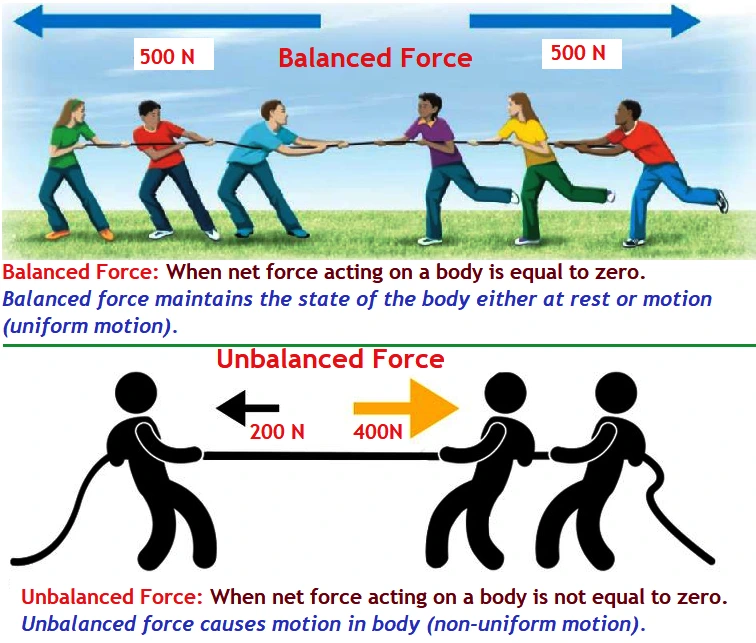
A force is a push or pull that changes the state of a body, its position, and the direction of motion of a body.
Force is a vector quantity.
SI Unit of force is newton(N).
Inertia
Inertia is the property of a body due to which its opposite change in its state is called inertia.
The inertia of a body depends on the mass of the body, and it is directly proportional to the mass of the body. Greater the mass of the body, greater will be its inertia.
Law of Inertia:
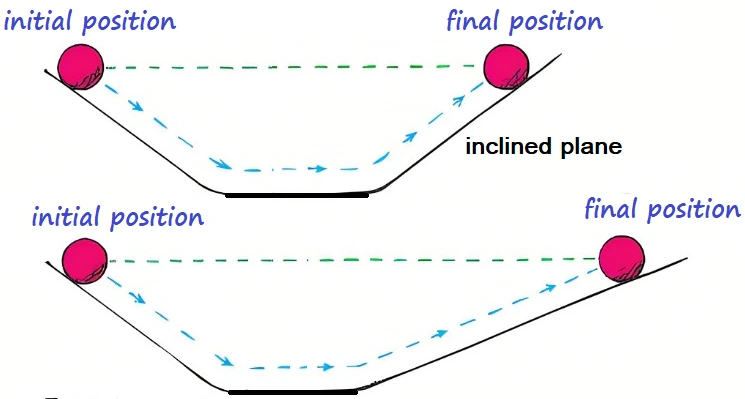
Galileo performed an experiment with an incline plane and a bob. On the basis of experimental observation, he gave the Law of Inertia.
A body moving with a certain speed along a straight path will continue to move with same speed along the same straight path in the absence of external forces.
Types of Inertia:
Inertia is of three types,
(1) Inertia of rest
(2) Inertia of motion
(3) Inertia of direction
Inertia of Rest:
The tendency of a body due to which it opposes change in its state, from rest to motion, is called inertial of rest.
Examples:
- A person standing in a bus falls backward when the bus suddenly starts moving forward.
- When a horse suddenly starts running the rider falls backward.
- Dust is removed from hanging carpet by beating it with a stick when we beat carpet it suddenly move forward while the dust particle tends to remain at rest due to inertia of rest and so fall of.
- When we shake the branch of a tree it’s fruits and dry leaves fall down.
Inertia of Motion:
The tendency of a body due to which it opposes change in its state, from motion to rest, is called inertial of motion.
Examples:
- When a moving bus suddenly stops, a person sitting in it falls forward.
- When a horse running fast suddenly stops, the rider is thrown forward if he is not firmly seated.
- An athlete runs for a certain distance before taking a long jump.
- A ball thrown upward in a moving train comes back into the thrower’s hands.
Inertia of Direction:
The property of a body due to which it opposes change in its direction of motion is called inertia direction.
Examples:
- When a bus takes a sharp turn, a person sitting in the bus experiences a force acting away from the centre of the curve path due to his tendency to move in the original direction.
- A stone thrown in horizontal direction in the air, moves straight in horizontal direction due to its inertia.
- During the sharpening of a knife, the sparks coming from the grind stone fly tangentially to the rim of the rotating stone. This is due to inertia of direction.
- When a vehicle moves, the mud stuck to its wheels goes tangential.
Important short answer type questions
Why do the bodies of less mass require less effort to bring them into motion?
Answer: Inertia of body is directly proportional to its mass. so lesser the mass, lesser is the opposition of change in its state from rest to motion.
Why do the passengers falls in backward direction when a bus suddenly starts moving from the rest position?
Answer: When the bus suddenly starts moving, the lower part of the passenger’s body, which is in contact with the bus, begins to move while the upper part of the passenger’s body remains at rest due to inertia of rest. Since the lower part moves forward as the bus moves, passengers fall backward.
Why are passengers thrown forward from their seats when a speeding bus stops suddenly ?
Answer: When the bus is in removing condition due to inertia of motion, the whole body part of the passenger is in moving condition, but as the bus stops, the lower part of the body stops suddenly as it is in contact with the bus, while the upper part, due to inertia of motion, is in moving condition. That’s why passengers are thrown forward from their seats when a bus stops suddenly.
Why do the blades of an electric fan continue to rotate for sometime after the current is switched off?
Answer: Due to inertia of motion.
Why it is difficult to put a cycle into motion then to maintain its motion?
Answer: Due to inertia of rest and motion
A body is acted upon by number of external force. can it remain at rest?
Answer: yes, if number of balance forces acting on it so that there resultant force is equal to zero.
If the net force acting on a body be zero, will the body remain necessarily in rest position ? explain.
Answer: No, when the net force acting on a body is zero, the body may be in a state of uniform motion along a straight line or in a resting condition.
Force and Laws of Motion QUIZ-1
MY YouTube Channel Link : 👉🖱 https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCGpC7nWE0-bBv9I53MM8qjQ
Force and Laws of Motion, Force and Laws of Motion, Force and Laws of Motion, Force and Laws of Motion, Force and Laws of Motion, Force and Laws of Motion, Force and Laws of Motion, Force and Laws of Motion, Force and Laws of Motion