Factors affecting acceleration due to Gravity
- Variation of g with altitude or height:
- Variation of g with depth:
- Variation of g with the shape of the earth:
- Variation of g with latitude or rotation of the earth:
Variation of g with altitude or height:
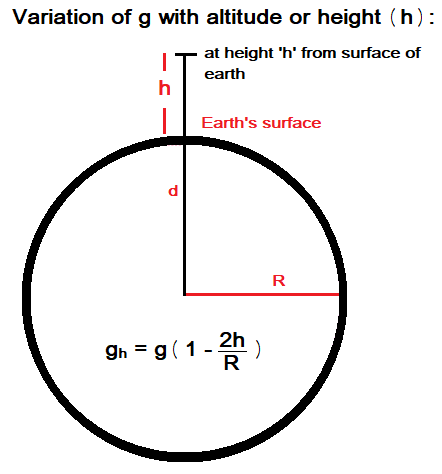
The value of acceleration due to gravity decreases with increase in height that is why the value of g is less at mountains then at plains. The value of acceleration due to gravity (gh) at height h,
gh = g (1- 2h / R)
g = 9.81 m/s2 = average value of acceleration due to gravity.
- h = height at which g is measured
- R = Radius of earth
Variation of g with depth:
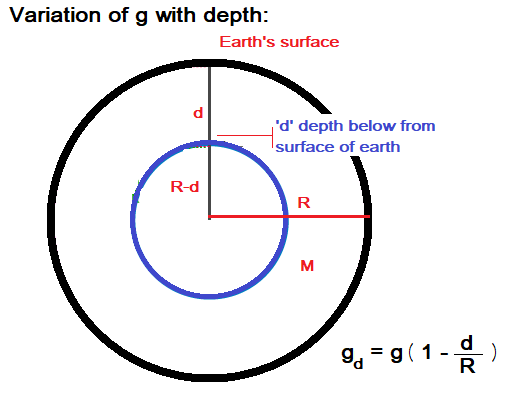
Acceleration due to gravity decreases with an increase in depth d. That is why the acceleration due to gravity is less in mines than on the earth’s surface, and at the centre of the earth the value of acceleration due to gravity becomes zero. The value of acceleration due to gravity (gd) at depth d,
gd = g (1- d / R)
- d = depth at which g is measured
- R = Radius of earth
Variation of g with the shape of the earth:
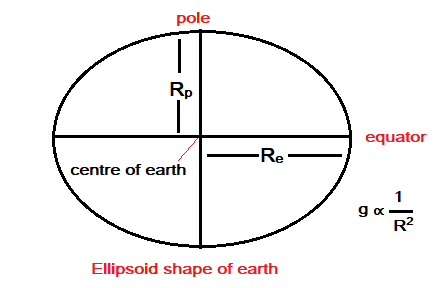
Since the Earth is not a perfect sphere. Its radius is less at the pole than at the equator. The radius of the Earth is greater at its equator (Re) than it is at its pole (Rp).
g = GM/R2
- M = Mass of earth
- G = Universal Gravitational Constant
- R = Radius of earth
The value of acceleration due to gravity ‘g’ is minimum at the equator and maximum at the poles. That is why the weight of a body increases when it is taken from the equator to the pole. The variation of g between the poles and the equator is about 0.5%.
Variation of g with latitude or rotation of the earth:
As we move from the equator to the pole, the value of acceleration due to gravity increases because of rotation of the earth.
Question 1:
What are the various factors on which the value of ‘g’ at any point on the earth depends?
Ans: The value of g changes from place to place, it depends on
(i) altitude
(ii) depth
(iii) shape of the earth
(iv) rotation of the earth