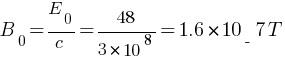EM Waves NCERT Solutions
EM Waves NCERT Solutions
What physical quantity is the same for X-rays of wavelength10–10m, red light of wavelength 6800 Å and radio-waves of wavelength 500m?
Ans: Speed of all electromagnetic wave is same 3 × 108 m/s.
A plane electromagnetic wave travels in vacuum along z-direction. What can you say about the directions of its electric and magnetic field vectors? If the frequency of the wave is 30 MHz, what is its wavelength?
Ans: Electric and magnetic field vectors are perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation. Electric and magnetic field vectors in the x-y plane are present in electromagnetic waves travelling in vacuum along the z-direction.
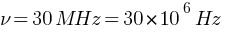
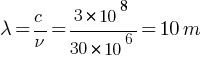
A radio can tune in to any station in the 7.5 MHz to 12 MHz band. What is the corresponding wavelength band?
Ans: Corresponding wavelength band (range of wavelength) =?
initial frequency 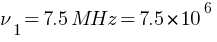 Hz
Hz
final frequency 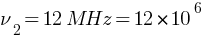 Hz
Hz
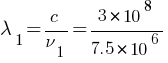 = 40m
= 40m
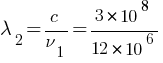 = 25m
= 25m
corresponding wavelength band = 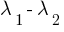 = 40m – 25m
= 40m – 25m
A charged particle oscillates about its mean equilibrium position with a frequency of 109 Hz. What is the frequency of the electromagnetic waves produced by the oscillator?
Ans: The frequency of the electromagnetic waves produced by the oscillator is equal to the frequency of oscillating charged particles, 109 Hz.
The amplitude of the magnetic field part of a harmonic electromagnetic wave in vacuum is B0 = 510 nT. What is the
amplitude of the electric field part of the wave?
Ans: B0 = 510nT = 510 × 10-9 T, c = 3 ×108 m/s
E0 = c B0
E0 = 3 ×108 × 510 × 10-9 = 153 N/C
Suppose that the electric field amplitude of an electromagnetic wave is E0 = 120 N/C and that its frequency is n = 50.0 MHz. (a) Determine, B0,w, k, and l. (b) Find expressions for E and B.
Ans: E0 = 120 N/C , frequency = 50.0 MHz
(a) E0 = c B0
[pmath size = 15] B_0 = ? omega =?, k =?, lambda =? [/pmath]
[pmath size = 15] B_0 = E_0 / c = 120 / 3 * 10^8 = 4 * 10^7 [/pmath]
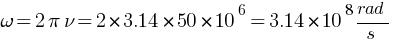
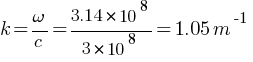
![lambda = v / nu = {3 * 10^8} / {50 * 10^6} = 6 m ] lambda = v / nu = {3 * 10^8} / {50 * 10^6} = 6 m ]](https://mywebpathshala.com/wp-content/plugins/wpmathpub/phpmathpublisher/img/math_972_c493292a1eb146c1079541ec5b02faa4.png)
(b)
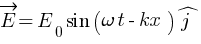
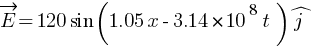 N/C
N/C
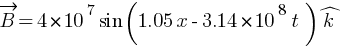 T
T
In a plane electromagnetic wave, the electric field oscillates sinusoidally at a frequency of 2.0 × 1010 Hz and amplitude 48 Vm–1.
(a) What is the wavelength of the wave?
(b) What is the amplitude of the oscillating magnetic field?
👉🖱️ (c) Show that the average energy density of the E field equals the average energy density of the B field. [c = 3 × 108 m s–1.]
Ans: Given: frequency = 2.0 × 1010 Hz, E0 = 48 Vm–1
(a) wavelength of the wave = ?
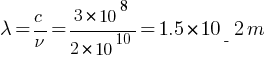
(b) Amplitude of the oscillating magnetic field = ?