Electrostatic force and Coulombs law
Electrostatic force:
Electrostatic force is one of the fundamental force in nature, acting between electrically charged particles due to their electrostatic interactions.
Properties of Electrostatic force:
- Electrostatic force is an attractive or repulsive in nature. Like charges repel each other, while unlike (opposite) charges attract.
- It is a central force – a charged body attracts another charged body towards its centre.
- Electrostatic force is a conservative force, which means that the work done by electrostatic force to move a charge particle from one point to another point is path independent.
- It obey Newton’s III Law. Force applied on body 1 due to body 2 is equal to force applied on body 2 due to body 1.
- .Electrostatic force is one of the four fundamental forces of nature, along with gravity, the weak nuclear force, and the strong nuclear force. Relative strength of Fundamental Forces in Nature : FG : FWN : FE: FSN = 1: 1025 :1036 : 1038

Table of Contents
Applications of concept of Electrostatic force:
- Electrostatic Precipitators: The electrostatic force is used in electrostatic precipitators to remove particulate matter from industrial exhaust gases. Electrostatic precipitators use high-voltage electricity to ionize particles in the exhaust gas, and then collect them on a charged surface.
- Inkjet Printers: Electrostatic force is used in inkjet printers to propel ink droplets onto paper. The ink is charged with an electrode, and the paper is given the opposite charge. As the ink droplets are released, they are attracted to the oppositely charged paper and deposited onto the surface.
- Spray Painting: Electrostatic force is used in spray painting to attract paint particles to a grounded object. The paint is charged with an electrode and sprayed onto the object. The object is then grounded, creating an attractive force between the charged paint particles and the object.
- Van de Graaff Generator: The Van de Graaff generator is a device that uses electrostatic force to generate high voltages. The generator consists of a metal sphere connected to a motor that rotates a rubber belt. As the belt rotates, it picks up electrons from a comb, which are transferred to the metal sphere. The accumulated charge creates a high voltage between the sphere and ground.
- Photocopiers: Electrostatic force is used in photocopiers to create an image on a photosensitive drum. The drum is charged with an electrode, and a light is shone on the drum, creating an electrostatic image of the original document. The image is then transferred to paper using an oppositely charged surface.
- Electrostatic Discharge Protection: Electrostatic discharge (ESD) is a common problem in electronics, where static electricity can damage sensitive components. Electrostatic force can be used to protect against ESD by grounding or shielding electronic components.
Coulomb’s law :
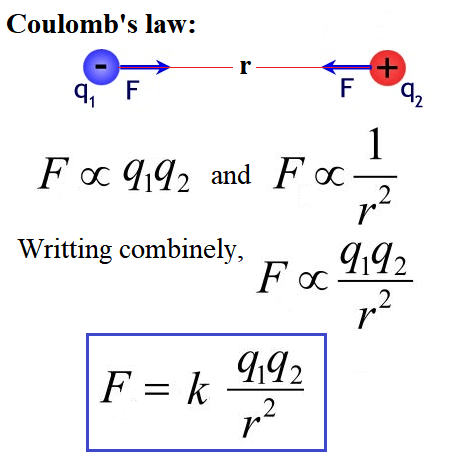
Coulomb’s law is a fundamental law of electrostatics that describes the relationship between the electric charges of two particles and the force of attraction or repulsion between them. It was first formulated by French physicist Charles-Augustin de Coulomb in 1785.
The law states that the Electrostatic force acting between two point charges is directly proportional to the product of magnitude of both charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
The mathematical expression for Coulomb’s law is:
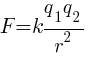
Where, k is a proportionality constant called Electrostatic force constant or Coulomb’s constant, value depends on nature of medium.
F is the Electrostatic force between the two point charges.
q1 and q2 are the magnitudes of the charges.
r is the distance between both charges
For air or vacuum,
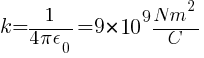
Coulomb’s law in vector form:
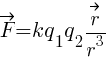
Limitations of Coulomb’s law:
- It applicable for stationary charges only.
- It applicable only for point charges. ( It can be applied to large size charged object but with certain modifications).
Important questions based on Topic
What is electrostatic force?
Ans: Electrostatic force, also known as Coulombic force, is a fundamental force of nature that arises from the interaction between electric charges.
How does electrostatic force work?
Ans: Electrostatic force is an attractive or repulsive force between two charged objects. Like charges repel each other, while opposite charges attract.
What is Coulomb’s law?
Ans: Coulomb’s law describes the strength of the electrostatic force between two charged objects, which is directly proportional to the product of the charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
Is electrostatic force a conservative force?
Ans: Yes, electrostatic force is a conservative force, which means that the work done by the force to move a charge from one point to another is independent of the path taken.
What are some examples of electrostatic force in everyday life?
Ans: Examples of electrostatic force in everyday life include the attraction of a balloon to a person’s hair, the formation of lightning, and the use of static electricity to power photocopiers and paint sprayers.
Can electrostatic force be shielded?
Ans: Yes, electrostatic force can be shielded by the presence of other charged objects or conductive materials, as in the case of Faraday cages.
How is electrostatic force related to electromagnetism?
Ans: Electrostatic force is one of the four fundamental forces of nature, and it plays a crucial role in the study of electromagnetism, which is the study of the interaction between electric and magnetic fields.
How does the dielectric constant of a material affect the electrostatic force between two charged objects?
Ans: The dielectric constant of a material affects the electrostatic force by reducing the force between charged objects that are separated by a dielectric material. This is because the dielectric material reduces the electric field strength between the charged objects.
How does the distance between two charged objects affect the electrostatic force between them?
Ans: The electrostatic force between two charged objects is inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. This means that as the distance between the charged objects increases, the force between them decreases.
How does the electrostatic force between two charged objects change if the charges on one of the objects is doubled?
Ans: The electrostatic force between two charged objects is directly proportional to the product of the charges. Therefore, if the charge on one of the objects is doubled, the force between the objects will also double.
What is the significance of the Coulomb constant in Coulomb’s law?
Ans: The Coulomb constant is a proportionality constant in Coulomb’s law that relates the electrostatic force between two charged objects to the product of their charges and the distance between them. The value of the Coulomb constant determines the strength of the force and depends on the units used to express the charges and distance.
Can two objects with the same charge ever attract each other?
Ans: No, two objects with the same charge will always repel each other because the electrostatic force between them will be repulsive.
If there is a large difference in magnitude of charges on two closely placed body, due to induction both charges may attracts.
What happens to the electrostatic force between two charged objects if the charges have opposite signs?
Ans: If the charges on two objects have opposite signs, the electrostatic force between them will be attractive, causing the objects to move toward each other.
What are the limitations of Coulomb’s law?
Ans: Limitations of Coulomb’s law are,
- It applicable for stationary charges.
- It applicable only for point charges. ( It can be applied to large size object but with certain modifications).
What is the relationship between electrostatic force and gravitational force?
Ans: Electrostatic force and gravitational force are both fundamental forces of nature, but they have different origins and characteristics. Electrostatic force arises from the interaction between electric charges, while gravitational force arises from the interaction between masses. The strength of electrostatic force is much greater than gravitational force for particles with the same charge/mass.
MY YouTube Channel Link : 👉🖱 https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCGpC7nWE0-bBv9I53MM8qjQ
Electrostatic force and Coulombs law, Electrostatic force and Coulombs law, Electrostatic force and Coulombs law, Electrostatic force and Coulombs law, Electrostatic force and Coulombs law, Electrostatic force and Coulombs law, Electrostatic force and Coulombs law, Electrostatic force and Coulombs law, Electrostatic force and Coulombs law, Electrostatic force and Coulombs law, Electrostatic force and Coulombs law, Electrostatic force and Coulombs law,
Electrostatic force and Coulombs law, Electrostatic force and Coulombs law, Electrostatic force and Coulombs law, Electrostatic force and Coulombs law, Electrostatic force and Coulombs law, Electrostatic force and Coulombs law
I enjoyed reading your piece and it provided me with a lot of value.
Thank you for your valuable feedback 😊.