Electromagnetic Waves Important Points
Electromagnetic Spectrum
| Name | Wavelength Range | Production | Uses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gamma Rays | < 10-12 m | Gamma rays produced in radio active decay of nucleus | In treatment of cancer & to carry out nuclear reactions. |
| x-rays | 10-9 m to 10-12 m | x-ray tubes or inner shell electrons | used as diagnostic tool in medical to find out fractures in bones & to find crack, flaws in metal part of machine |
| UV rays | 4 × 10-7 to 10-9 m | By very hot bodies like sun and by UV lamps | In water purifier in detection of forged documents & in food preservation |
| Visible light | 7 × 10-7 m to 4 × 10-7m | to by accelerated tiny (electrons) charge particles | to see every thing around us |
| IR rays | 10-3 m to 4 × 10-7 m | due to vibration of atoms | in green houses to keep plant warm, to reveal secret writings on walls, in photography during fog and smoke |
| Microwaves | 10-1 m to 10-3 m | produced in klystron Valve and magnetron Valve | In RADAR & in microwave ovens |
| Radio waves | > 0.1 m | by accelerated charged particles excited electrical circuits | In radio telecommunication system & in radio astrology |
Table of Contents
Electromagnetic Waves Important Points

- EM waves are produced by accelerated charged particles only if there is a change in speed; if the charged particle moves in a circular path without changing its speed, then there will be no electromagnetic wave produced by it where there is no change in speed.
- Electric field and magnetic field vectors oscillate with the frequency of oscillating charge particles.
- Properties of electromagnetic waves-
- transverse in nature.
- can travel through vacuum.
- material not required for its propagation.
- speed of EM wave v = E / B = E0 / B0
- speed of EM waves in vacuum, c = 1 / √(μo єo) = 3 x 108 m/s.
- speed of EM waves in a medium, v = 1 / √(μ є)
- In an electromagnetic spectrum, different waves have different frequency and wavelengths.
- Penetration power of electromagnetic waves depends on frequency. Higher, the frequency larger the penetration power.
* Wavelength 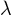 and frequency
and frequency 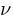 are related with each other
are related with each other 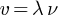 . Here v is the wave velocity.
. Here v is the wave velocity.
- A wave travelling along + x axis is represented by,
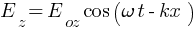
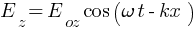
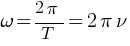
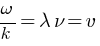 wave speed
wave speed
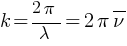
Wave number 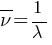
Displacement current (Id) :
The Current which is produced due to time varying electric field or electric flux.
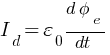 ,
, 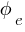 is the electric flux.
is the electric flux.
Modified Ampere’s Circuital Law by Maxwell –
∮ 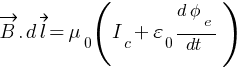 ,
,
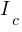 is the conduction current.
is the conduction current.
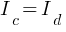
👉🖱️ बेसिक शिक्षा के लिए महत्वपूर्ण वेबसाइट
Electromagnetic Waves Important Points, Electromagnetic Waves Important Points, Electromagnetic Waves Important Points, Electromagnetic Waves Important Points