Electric Field due to a Point Charge
Electric Field
The region surrounding a charge particle in which another charge particles feels an electrostatic force is called electric field.
The knowledge of electric fields has many practical applications in technology and everyday life. It’s concept used in the manufacturing of electronic devices such as capacitors, transistors, and electric motors. One of its most important uses is in medical diagnosis, using imaging techniques such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), which uses a strong magnetic field and radio waves to create images of the body’s internal structures so that doctors can see abnormalities in the body.
Electric fields also play a critical role in the behavior of charged particles, such as electrons and ions. They are essential in understanding the behavior of plasma, which is a state of matter that consists of a gas of charged particles. Electric fields are also used in particle accelerators, which use high-energy electric fields to accelerate charged particles to very high speeds.

Table of Contents
Electric field intensity (E):
Strength of electric field is a measured in terms of intensity of Electric field. Intensity of Electric field at a point is equal to electrostatic force experienced per unit test charge (q0) in the electric field.
The magnitude of the electric field intensity is given by the formula:
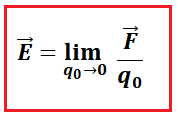
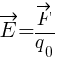
- Where, q0 is the magnitude of test charge
- E is the electric field intensity.
- F is the force acting on the test charge.
We can write formula in scalar form as,
E = F / q0
- The electric field intensity is a vector quantity, meaning that it has both magnitude and direction at every point in space. Direction of electric field intensity is away from positive charge.
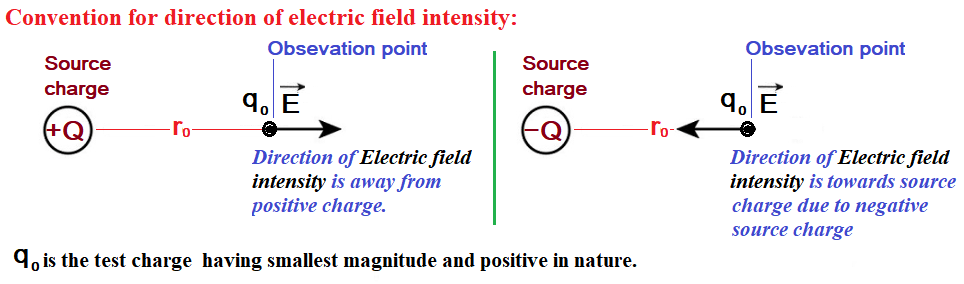
| Test charge (q0) : |
|---|
| A test charge is a point charge that is used to test or check the strength of the electric field due to another charge. A test charge is usually considered positive and has a unit magnitude. The test charge should have the smallest possible magnitude so that it doesn’t influence the electric field of the charge particle, whose electric field strength is being tested or checked. |
SI unit of electric field intensity:
The SI unit of electric field intensity is volts per meter (V/m). This means that one volt of potential difference between two points separated by one meter produces an electric field intensity of one volt per meter at any point in between.
Electric field intensity due to a point charge:
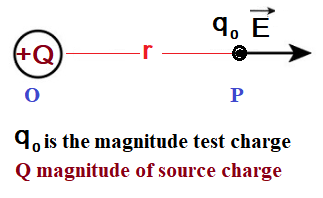
Consider a charge ‘Q’ (source charge) is kept at point O in space. There is an observation point P at a distance ‘r’ from it. Where we have to find electric field intensity due to a point charge Q. Put a test charge of magnitude (q0) at observation point.
Electrostatic force experienced by test charge using Coulomb’s law
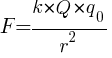
Where, F is the electric force between two point charges Q and q0, r is the distance between them, and k is the Coulomb constant, which is approximately equal to 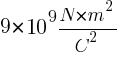 .
.
Electric field intensity at point O,
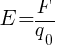
Substituting the expression for F from Coulomb’s law, we get:
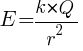
This expression gives the electric field intensity due to a point charge Q at a distance r from it.
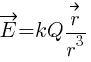
- The electric field intensity is
- (i) proportional to the magnitude of the point charge Q (source charge) not test charge magnitude (q0).
- (ii) inversely proportional to the square of the distance r from the point charge.
Questions from the Topic
What is an electric field?
A: An electric field is a region around an electrically charged object where the electrostatic force exerted on other charged objects can be observed.
Q: How is an electric field measured?
A: Electric field strength is measured in units of volts per meter (V/m) using an electric field meter or probe.
What is the formula for electric field?
A: The electric field is defined as the force per unit charge acting on a charged particle. The formula for electric field is E = F/q, where E is the electric field strength, F is the force on the charge q, and q is the magnitude of the charge.
What is the direction of an electric field?
A: The direction of the electric field is the direction of the force that would be exerted on a positively charged test charge placed in the field.
Q: What is the difference between electric field and electric potential?
A: The electric field is a vector field that describes the force experienced by a charged particle, while electric potential is a scalar field that describes the potential energy per unit charge at a point in space.
Q: How is an electric field created?
A: An electric field is created by a charged object or collection of charged objects, which can either attract or repel other charged objects in the surrounding area.
Q: What is the relationship between electric field and electric charge?
A: Electric field is created by the presence of electric charge, and the strength of the electric field is proportional to the magnitude of the charge creating it.
What is the SI unit of electric field?
A: The SI unit of electric field is volts per meter (V/m).
Can an electric field exist in a vacuum?
Answer: Yes.
Q: How is an electric field represented?
A: An electric field is represented using field lines that indicate the direction of the force that would be exerted on a small positive test charge placed at any point in the field. The field lines emerge from positive charges and terminate at negative charges.
Q: What is the formula for the electric field due to a point charge?
A: The electric field due to a point charge is given by the formula E = kq/r^2, where E is the electric field, k is Coulomb’s constant (8.99 x 10^9 N*m^2/C^2), q is the charge of the point charge, and r is the distance from the point charge to the point where the electric field is being measured.
MY YouTube Channel Link : 👉🖱 https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCGpC7nWE0-bBv9I53MM8qjQ
Electric Field due to a Point Charge, Electric Field due to a Point Charge, Electric Field due to a Point Charge, Electric Field due to a Point Charge, Electric Field due to a Point Charge, Electric Field due to a Point Charge, Electric Field due to a Point Charge, Electric Field due to a Point Charge, Electric Field due to a Point Charge, Electric Field due to a Point Charge, Electric Field due to a Point Charge, Electric Field due to a Point Charge
Learn easy electric field class 12 , Learn easy electric field class 12 , Learn easy electric field class 12 , Learn easy electric field class 12 , Learn easy electric field class 12 , Learn easy electric field class 12 , Learn easy electric field class 12 , Learn easy electric field class 12
Please provide me with more details on the topic
Your articles are very helpful to me. May I request more information?