Unit 07: Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
Hello, readers 😊! Here we will learn important concepts from 12th class Physics Unit 07: Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter. This webpage consists notes, Important questions, previous year questions numerical and quizzes. Radiation has dual nature wave nature as well as particle nature.
The dual nature of radiation and matter refers to the idea that both radiation and matter have properties of both waves and particles.
In the case of radiation (such as light), it was found that it exhibited wave-like behavior when it passed through a diffraction grating, but also displayed particle-like behavior when it was absorbed or emitted by matter. This was described by the wave-particle duality, where light can be described as both a wave and a particle, depending on the experiment being performed.
Similarly, matter (such as electrons) was found to exhibit both wave-like and particle-like behavior. When electrons were passed through a double-slit experiment, they exhibited wave-like behavior in the form of an interference pattern. But when they were detected, they displayed particle-like behavior by being detected at a specific point on the screen.
This dual nature of radiation and matter is a fundamental aspect of quantum mechanics, and is a fundamental principle of modern physics. It has been confirmed by numerous experiments and is considered to be a cornerstone of our understanding of the universe.
Table of Contents
Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter INDEX

Electron Emission
The phenomenon, in which electrons are ejected from a metallic surface when an adequate amount of energy is supplied to it, is called electron emission.
- Electron emission may be of the following type,
- Thermionic Emission
- Field Emission or Cold Cathode Emission
- Photoelectric Emission
- Secondary Emission
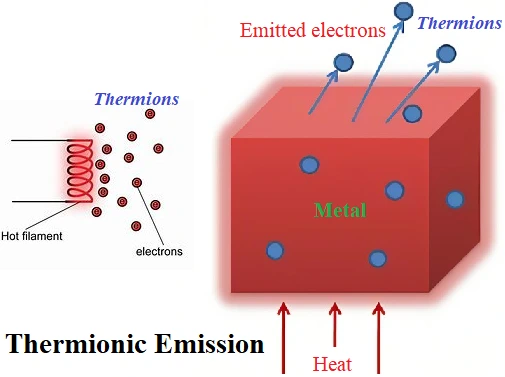
(1) Thermionic Emission:
Emission of electrons by heating a metal. Emitted electrons are called thermions or thermo-electrons.
When a metal is heated, energy is supplied to it. If this energy is more than the binding energy of electrons, electrons are ejected
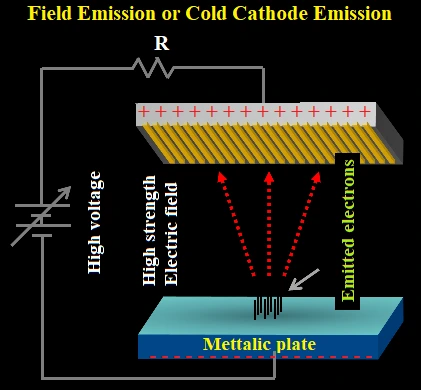
(2) Field Emission or Cold Cathode Emission:
When a metal surface is subjected to very high electric field (103-108 V/m) electrons are emitted from metal surface. Emitted electrons are called electrons.
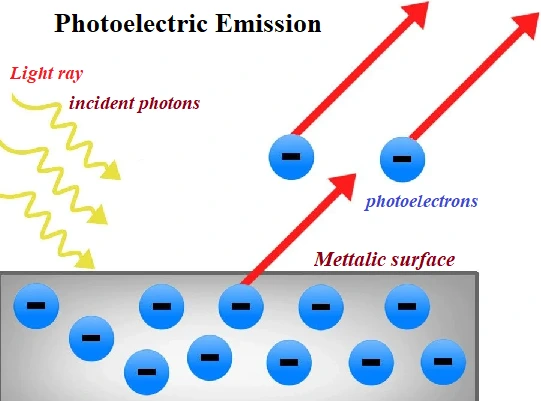
(3) Photoelectric Emission:
Electrons are emitted from metal surface when electromagnetic radiation of suitable frequency falls on it. Emitted electrons are called photoelectrons.
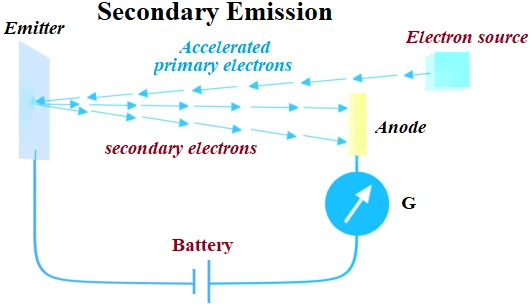
(4) Secondary Emission:
When fast moving electrons strikes to metal surface, electrons are emitted such electrons are called secondary electrons.
Work Function (ɸₒ)
The minimum amount of energy required by an electron to just escape from the metal surface is called the work function.
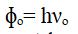
νₒ – the threshold frequency of incident radiation, h – Plank’s constant
Unit of Work Function:
The unit of work function is electron-volts (eV) or joules (J).
Factors affecting Work function (ɸₒ) of metal:
- The nature of the metal: The greater the metallic nature (tendency to lose electrons easily) of a metal, the lesser its work function. Cesium metal has the lowest work function and Platinum metal has the highest.
- The condition of the metal surface: If a metal’s surface is rough or rusted, it is difficult to remove an electron from it, so its work function is greater.

Important questions from Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
What is electron emission?
Ans: Electron emission is the process by which electrons are released from a material or surface, often due to an external stimulus such as heat, light, or an electric field.
What are the different types of electron emission?
Ans: There are several types of electron emission, including thermionic emission, photoemission, field emission, and secondary electron emission.
What is thermionic emission?
Ans: Thermionic emission is the emission of electrons from a material due to heating it to a high temperature. This process is commonly used in vacuum tubes and electron guns.
What is photoemission?
Ans: Photoemission is the emission of electrons from a material when it is exposed to light. This phenomenon is used in devices such as photodiodes and solar cells.
What is field emission?
Ans: Field emission is the emission of electrons from a material due to the application of a high electric field. This process is used in devices such as field-emission displays and electron microscopes.
What is secondary electron emission?
Ans: Secondary electron emission is the emission of electrons from a material due to the impact of high-energy particles such as electrons or ions. This process is important in a variety of applications, including particle detectors and plasma physics.
What is the work function of a material?
Ans: The work function of a material is the minimum energy required to remove an electron from its surface. This parameter is an important factor in determining the ease with which electrons can be emitted from a material.
Every metal has a definite work function, why do photoelectrons not come out with the same energy of incident radiation if incident radiation is monochromatic? Why is there an energy distribution of photo electrons?
Answer : The work function is the minimum amount of energy required by an electron to escape from the metallic surface; this energy corresponds to the highest energy level of the conduction band. All the electrons in metal do not belong to these categories; they occupy a continuous band of energy levels. So, for the same monochromatic incident radiation, electrons knocked off from different levels come out with different energies. Hence, photoelectrons have an energy distribution, and not every emitted electron has the same energy.
How does the work function influence the kinetic energy of electrons liberated during the photoelectric emission?
Answer: An increase in work function decreases kinetic energy.
What is the unit of work function?
Ans: The unit of work function is electron-volts (eV) or joules (J).
How is work function related to electron emission?
Ans: Work function is the minimum energy required to remove an electron from the surface of a material. Therefore, the energy of incident photons or particles must exceed the work function in order for electron emission to occur.
How is work function related to the energy of emitted electrons?
Ans: The kinetic energy of the emitted electrons is equal to the energy of the incident photons or particles minus the work function of the material.
How can work function be measured?
Ans: Work function can be measured using techniques such as photoemission spectroscopy or Kelvin probe force microscopy.
What factors can affect the work function of a material?
Ans: The work function of a material can be affected by factors such as the chemical composition of the material, the crystal structure, the surface cleanliness, and the presence of impurities or defects.
What are some applications of work function?
Ans: Work function plays a critical role in many technological applications, such as solar cells, electronic devices, and materials science. It is also used in surface science to study the properties of materials and their interactions with other materials.
Important Questions for Board Exams
Stay updated and get important questions here.
🖱️👉 Important Questions & HOTs Numerical ↗
MY YouTube Channel Link : 👉🖱 https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCGpC7nWE0-bBv9I53MM8qjQ
निपुण भारत: मिशन प्रेरणा फेज-2
Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter, Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter, Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter, Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter, Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter, Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
Great topic, please keep it up I really enjoy reading these type articles.