Hello, readers 😊! Here you can learn important questions from 12th class Physics Unit 07: Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter. This webpage contains Important questions, previous year questions and numerical from board exams. Dual Nature Important Questions
Dual Nature Important Questions
Table of Contents
A good mirror reflects 80% of light incident on it. Which of the following is correct ?
(a) Energy of each reflected photon decreases by 20%.
(b) Total no. of reflected photons decreases by 20%. Justify your answer.
Ans: (b) Total no. of reflected photons decreases by 20%.
Why in a photocell the cathode is coated with alkali metals ?
Ans: Lower work function, sensitive to visible light.
Name the phenomenon which shows quantum nature of electromagnetic radiation.
Ans: Photoelectric effect.
The Stopping potential in an experiment on photo electric effect is 1.5V : What is the maximum K.E. of photoelectrons emitted.
Ans: (K.E)max = eV0
(K.E.)max = 1.6 × 10-19 × 1.5 = 2.4 × 10-19 J
A metal emits photoelectrons when red light falls on it. Will this metal emit photoelectrons when blue light falls on it? Why?
Ans: Yes, blue light has higher frequency hence possess higher energy.
What is the de-Broglie wavelength of a 3 kg object moving with a speed of 2m/s?
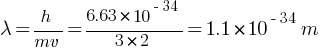
What factors determine the maximum velocity of the photoelectrons from a surface?
Ans: (a) frequency of incident radiation (b) work function of surface.
How will you justify that the rest mass of photons is zero?
According to the relativistic theory relation, the mass of the moving particle (here photon) is computed as
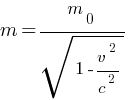
here, m0 = rest mass of particle
m = mass of particle at velocity v
v = velocity of particle
c = speed of light
for photon at rest condition, v = 0 m = ?
putting these values in above equation,
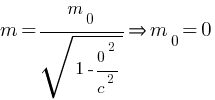 Thus rest mass of photon is zero.
Thus rest mass of photon is zero.
Why is the wave theory of light not able to explain the observed features of the photoelectric effect? Explain. How does photon picture resolve this problem?
Answer: Wave theory of light is not able to explain the observed features of photoelectric effect because,
- According to wave theory, the kinetic energy of photoelectrons must depend on the intensity of incident light, but it is experimentally observed that the kinetic energy of photoelectrons does not depend on the intensity of incident light.
- According to wave theory, light of any frequency can emit electrons from a metallic surface if the intensity of the light is sufficient to provide the necessary energy for electron emission; however, experimental observations show that light with a frequency less than the threshold frequency cannot emit electrons, regardless of the intensity of incident light.
- According to wave theory, the energy transferred by light waves will not go to a particular electron, but it will be distributed uniformly to all electrons present on the illuminated surface. Therefore, electrons will take some time to collect the necessary energy for their emission. The time for emission will be longer for light of lower intensity and vice versa. But experimental observations show that the emission of electrons takes place instantaneously after the light is incident on the metal, whatever the intensity of light may be.
According to photon picture of radiation, when light interact with matter it behaves like particle known as photon. Photon consist of small packets of energy called quanta each having energy h . Further photon pictures of light can be explained by Einstein’s photoelectric equation
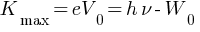 This equation explains all experimentally observed features of the photoelectric effect.
This equation explains all experimentally observed features of the photoelectric effect.
Every metal has a definite work function, why do photoelectrons not come out with the same energy of incident radiation if incident radiation is monochromatic? Why is there an energy distribution of photo electrons?
Answer : The work function is the minimum amount of energy required by an electron to escape from the metallic surface; this energy corresponds to the highest energy level of the conduction band. All the electrons in metal do not belong to these categories; they occupy a continuous band of energy levels. So, for the same monochromatic incident radiation, electrons knocked off from different levels come out with different energies. Hence, photoelectrons have an energy distribution, and not every emitted electron has the same energy.
Explain why the saturation current in photoelectric effect experiments with light of one frequency and intensity is independent of anode potential?
Answer: In the state of saturation current, all the electrons emitted from the cathode (for the given frequency and intensity) reach the anode and constitute the current. Further increases in anode potential will not increase the number of photoelectrons emitted, and thus the current will not change.
What is rest mass of photon?
Answer: Rest mass of photon is zero.
Why the wave theory of light is unable to explain the most basic features of photoelectric emission?
Write the properties of the photon based on Particle theory of Light.
Do all photons have same mass?
Answer: No. Photons have different masses according to their frequency. Although their rest mass is zero.
If the wavelength of an electromagnetic radiation is doubled, what will happen to the energy of photons?
Answer: Energy of each photon is give by,
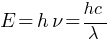
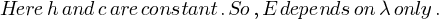
From above relation it is clear that if wavelength of radiation is doubled then energy of radiation becomes half.
In the wave picture of light, the intensity of light is determined by the square of the amplitude of the wave. What determines the intensity of light in the photon picture of light?
Answer: In Photon picture of light, the intensity of light represents the number of photons incident per unit area per unit time.
For a chromatic radiation incident on a photosensitive surface, why do all photoelectrons not come out with the same energy? Give reason for your answer.
Answer: Each electron lies in conduction band of photosensitive material have different value of work function.
According to Einstein’s photoelectric equation
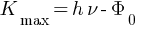
Kmax will be different because 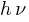 is constant but
is constant but 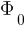 is different electrons for each electron.
is different electrons for each electron.
Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Test Paper
Time: 1:15 hr Class-XII PHYSICS (Theory )- 042 Max. Marks: 30
General Instruction
- All questions are compulsory
- There is no choice.
- What is the charge on metal in the photoelectric experiment? (01)
- What factors determine the maximum velocity of the photoelectrons from a surface? (01)
- Define the terms: ‘stopping potential ‘and threshold frequency’ in photoelectric emission. (01)
- You are given a 2F parallel plate capacitor. How would you establish and instantaneous displacement current of 1mA in the between its plates? (02)
- An electron and a proton are moving in the same direction and possess same kinetic energy. Find the ratio of de Broglie wavelengths associated with these particles. (02)
- Show how maximum kinetic energy of electrons emitted from a photosensitive surface varies with frequency of incident radiations. (02)
- Monochromatic light of frequency 6.0 x 1014 Hz is produced by a laser. The power emitted is 2.0 x 10-3 W.
- (a) What is the energy of a photon in the light beam?
- (b) How many photons per second, on the average, are emitted by the source? (02)
- Derive the expression for the de Broglie wavelength of an electron moving under a potential difference of V volt using de-Broglie hypothesis. (02)
- Describe Davisson-Germer experiment to establish the wave nature of electrons. Draw a labeled diagram of the apparatus used. (03)
- A capacitor of capacitance ‘C’ is being charged by connecting it across a dc source along with an ammeter. Will the ammeter show a momentary deflection during the process of charging? If so, how would you explain this momentary deflection and the resulting continuity of current in the circuit? Write the expression for the current inside the capacitor. (03)
- Draw a graph showing the variation of stopping potential with frequency of incident light in relation to photoelectric effect. Deduce an expression for the slope of this graph using Einstein’s photoelectric equation. (03)
- A particle A with a mass mA is moving with a velocity v and hits a particle B (mass mB) at rest (one dimensional motion). Find the change in the de-Broglie wavelength of particle A. treat collision as elastic. (03)
- Monochromatic light of wavelength 632.8nm is produced by helium – neon laser. The power emitted is 9.42mW.
- (a) Find the energy and momentum of each photon in the light beam.
- (b) How many photons per second, on the average, arrive at a target irradiated by this beam? (assume the beam to have uniform cross – section which is less than the target area), and
- (c) How fast does a hydrogen atom have to travel in order to have the same momentum as that of the photon? (05)
Dual Nature Important Questions, Dual Nature Important Questions, Dual Nature Important Questions, Dual Nature Important Questions, Dual Nature Important Questions, Dual Nature Important Questions, Dual Nature Important Questions, Dual Nature Important Questions, Dual Nature Important Questions, Dual Nature Important Questions, Dual Nature Important Questions, Dual Nature Important Questions, Dual Nature Important Questions, Dual Nature Important Questions, Dual Nature Important Questions, Dual Nature Important Questions, Dual Nature Important Questions
MY YouTube Channel Link : 👉🖱 https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCGpC7nWE0-bBv9I53MM8qjQ