Diode
Hello, readers! Here you can learn about Semiconductor Diode. A pn-junction diode is a two terminal semiconductor device that is used to rectify alternate current.
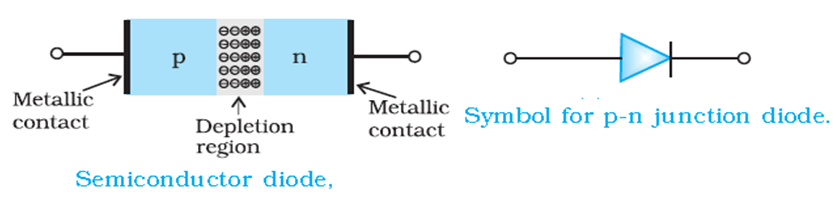
Semiconductor Diode
A pn-junction diode is a two terminal semiconductor device that is used to rectify alternate current.
A pn-junction diode allows current to flow in only one direction. PN-junction diode is active in forward bias only.
Important questions from the Topic
What is a semiconductor diode?
Ans: A semiconductor diode is a two-terminal electronic component that conducts current in one direction and blocks current in the opposite direction. It is made of a semiconductor material, such as silicon or germanium, and is commonly used in electronic circuits for rectification, voltage regulation, and signal detection.
How does a diode work?
Ans: A diode works by allowing current to flow in one direction while blocking it in the opposite direction. This is due to the presence of a p-n junction, where the p-type material has a surplus of positively charged holes and the n-type material has an excess of negatively charged electrons. When a voltage is applied across the diode, electrons flow from the n-type material to the p-type material, creating a depletion region where there are no free charges. In the forward bias condition, the voltage applied to the diode allows the electrons to cross the depletion region, resulting in current flow. In the reverse bias condition, the voltage applied to the diode opposes the flow of electrons, causing the diode to block current.
What are the different types of diodes?
Ans: There are many different types of diodes, including rectifier diodes, zener diodes, Schottky diodes, and light-emitting diodes (LEDs). Rectifier diodes are used to convert AC voltage to DC voltage, while zener diodes are used to regulate voltage. Schottky diodes have a lower forward voltage drop than other diodes, and are often used in high-speed circuits. LEDs are used to emit light in a range of applications, including displays, indicators, and lighting.
What is the voltage drop across a diode?
Ans: The voltage drop across a diode depends on the type of diode and the current flowing through it. For a silicon diode, the voltage drop is typically around 0.6 to 0.7 volts in the forward direction. For a germanium diode, the voltage drop is typically lower, around 0.2 to 0.3 volts. The voltage drop of a diode is important to consider when designing electronic circuits, as it can affect the overall performance and efficiency of the circuit.
What is reverse breakdown voltage?
Ans: Reverse breakdown voltage is the voltage at which a diode breaks down and starts to conduct in the reverse direction. This can happen if the reverse voltage applied to the diode is too high, causing a large enough electric field to overcome the depletion region and allowing current to flow in the reverse direction. Reverse breakdown voltage is an important parameter to consider when selecting a diode for a specific application, as exceeding this voltage can damage the diode or the circuit.
What is the difference between a rectifier diode and a zener diode?
Ans: While both rectifier diodes and zener diodes are types of semiconductor diodes, they have different functions. A rectifier diode is used to convert AC voltage to DC voltage by allowing current to flow in one direction only. A zener diode, on the other hand, is used as a voltage regulator to maintain a constant voltage across a load. When a zener diode is reverse-biased, it conducts in the reverse direction once a certain voltage (known as the zener voltage) is reached, which helps maintain a stable output voltage.
How does the doping concentration affect the behavior of a diode?
Ans: The doping concentration of a diode refers to the amount of impurities added to the semiconductor material during the manufacturing process. The doping concentration affects the size of the depletion region in the p-n junction, and thus the voltage required to forward bias the diode. A higher doping concentration results in a smaller depletion region, and therefore a lower voltage drop across the diode. Conversely, a lower doping concentration results in a larger depletion region and a higher voltage drop.
How can temperature affect the performance of a diode?
Ans: The performance of a diode can be affected by temperature in several ways. First, the forward voltage drop of a diode decreases as temperature increases, which can affect the efficiency of a circuit. Second, the reverse leakage current of a diode increases as temperature increases, which can affect the accuracy of voltage regulation in circuits that use zener diodes. Third, the maximum power dissipation of a diode is reduced at higher temperatures, which can lead to thermal runaway and failure of the device.