Hello, readers 😊! Here you learn about Mass defect, Binding energy of the nucleus, expression for Binding energy, Binding energy per nucleon, Significance of calculating binding energy per nucleon and Binding energy curve.
Mass defect (∆m)
The difference between the rest mass of a nucleus and the sum of the rest masses of its constituent particles (proton and neutron) is called mass defect.
What causes mass defects? Mass defect arises due to the fact that when protons and neutrons combine to form a nucleus, a very small amount of their masses is converted to binding energy according to Einstein’s mass-energy equivalence relation ∆E = ∆mc2 . That’s why the mass of a nucleus (a composite particle) is less than the combined mass of protons and neutrons (masses of constituent particles of a nucleus).
In a nuclear reaction, the number of protons and neutrons is constant before and after the reaction, but the binding energy changes.
mN = mass of nucleus
mp= mass of proton
mn = mass of neutron
Mass defect = total mass of nucleons – mass of nucleus = (mass of protons + mass of neutrons) – mass of nucleus
∆m = [ Zmp + (A-Z) mn] – mN
Table of Contents
Binding energy:
Binding energy is the amount of energy required to split a nucleus into its constituent particles, protons and neutrons, and separate them far enough apart so that they do not interact with each other.
Expression for Binding energy of nucleus:
When atom constituent particles combine to form atoms, a very small amount of their masses are destroyed completely and converted to binding energy. Their binding energy can be calculated with the help of Einstein’s Mass – Energy Equivalence ∆Ebinding = ∆mc2 = loss in mass × (speed of light) 2

Binding energy per nucleon: The amount of energy required to remove one nucleon from the nucleus.
(∆Eb)n = ∆Eb / A
AZ X
Binding Energy Curve
Binding energy curve is a plot of the binding energy per nucleon (∆Eb)n versus the mass number (A) for nuclei of different elements.
Variation of binding energy per nucleon as a function of mass number: Binding energy curve
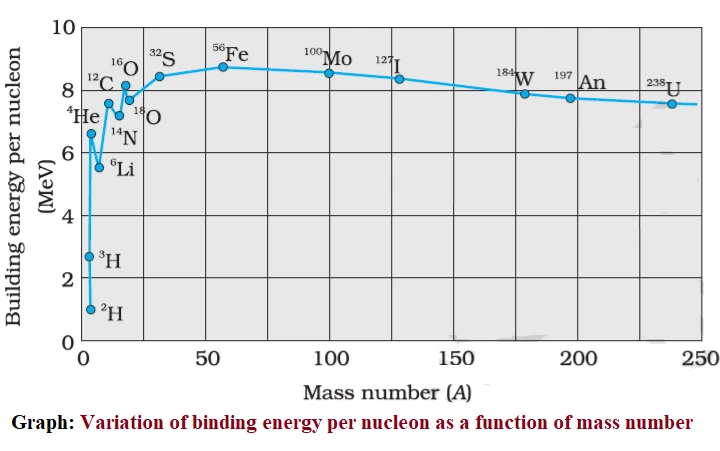
Important features Binding energy curve:
B.E. curve have following important features,
- The binding energy curve is a smooth line for all nuclei except for nuclei of He, C, O, Li, and N.
- In the range from mass number 2 to 20, there are well-defined maximum and minimum values of binding energy per nucleon. Maxima occur for 2He4, 6C12 and 8O16 and minima for 3Li6, 7N14 and 8O18.
- The element which has the highest value of binding energy per nucleon has the most stable nucleus, so iron 26Fe56 has the most stable nucleus as it has the highest binding energy per nucleon = 8.8 MeV/nucleon.
- From range mass number 40 to 120, the binding energy per nucleon increases to 8.5 MeV and then decreases due to Coulombic repulsion between protons inside the nucleus, making the nucleus the least stable.
- The binding energy per nucleon is lower for both light nuclei (A < 30) and heavy nuclei (A > 170), as they have less stable nuclei.
Significance of Binding energy curve:
Nuclear fission: B.E. per nucleon smaller than the middle one for heavier nuclei (A˃240) so unstable. When a heavy nucleus splits into the lighter nuclei, energy is liberated. This is the basis of the Atom Bomb.
Nuclear fusion: B.E. per nucleon is small for light nuclei (A˂10) so less stable. When two small nuclei combine to form heavy nuclei, energy is released. This is the basis of the hydrogen bomb.
Nuclear energy
The energy which is obtained from nuclear reactions is called nuclear energy.
Nuclear Reaction:
Nuclear Reaction:
- Nuclear fission: The phenomenon in which a heavy nucleus (A > 230) splits into two smaller nuclei and huge amount of energy is released, is called nuclear fission.
+ → + + 3 + Q
- Nuclear fusion: The phenomenon in which two light nuclei combine to form a single heavy nucleus and tremendous amount of energy is released, is called nuclear fusion.
11H + 11H → 21H + e+ + energy
MY YouTube Channel Link : 👉🖱 https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCGpC7nWE0-bBv9I53MM8qjQ
May I expand this? It’s a very eloquent post anyway, so kudos!