Atoms and Nuclei important questions
How does the distance of closest approach change?
Ans: Distance of closest approach is inversely proportional to the kinetic energy of the incident alpha particle. So, distance of closest approach is halved when the kinetic energy of alpha particle is doubled.
Table of Contents
In a hydrogen atom, if the electron is replaced by a particle which is 200 times heavier but has the same charge, how would its radius change?
Answer:
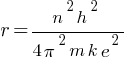
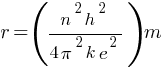
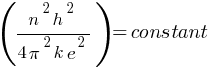
So, 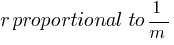
According to the above formula, the radius of a hydrogen atom is inversely proportional to the mass of an electron. so its radius will decrease to one upon 200 times the original radius with the increase in mass.
When an electron falls from higher energy to a lower energy level, the difference in the energies appear in the form of electromagnetic radiation. Why can’t it be emitted as other forms of energy.
Answer: This is because electron interacts only electromagnetically.
Atoms and Nuclei Test Paper
Time: 1:15 hr Class-XII PHYSICS (Theory )- 042 Max. Marks: 30
General Instruction
- All questions are compulsory
- There is no choice.
- What is Bohr’s quantization condition? (01)
- What is the energy possessed by an electron for n = ? (01)
- In Bohr’s theory of model of a Hydrogen atom, name the physical quantity which equals to an integral multiple of h/2Π? (01)
- What is the shortest wavelength and shortest frequency present in the Paschen series of spectral lines? (02)
- In a Geiger – Marsden experiment, calculate the distance of closest approach to the nucleus of Z=80, when an α – particle of 8MeV energy impinges on it before it comes momentarily to rest and reverses its direction. (02)
- Calculate the wavelength of Hα line in Balmer series of hydrogen atom, given Rydberg constant R= 1.0947 x 107 m-1. (02)
- Calculate the frequency of the photon which can excite an electron to -3.4 eV from -13.6 eV. (02)
- Define the terms excitation energy and ionization potentials. (02)
- The energy of the electron in the ground state of hydrogen atom is – 13.6eV.
- (a) What does the negative sign signify?
- (b) How much energy is required to take an electron in this atom from the ground state to the first excited state? (03)
- Show that the speed of an electron in the innermost orbit of H-atom is 1/137 times the speed of light in vacuum. (03)
- What is the energy level diagram for an atom? Calculate the energies of the various energy levels of a hydrogen atom and draw an energy level diagram for it. (03)
- Using postulates of Bohr’s theory of hydrogen atom, show that
- (a) The radii of orbits increases as n2, and
- (b) The total energy of the electron increases as 1/n2, where n is the principal quantum number of the atom. (05)
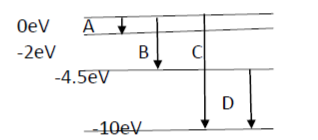
- The energy levels of an atom are as shown below.
- a) Which of them will result in the transition of a photon of wavelength 275 nm?
- b) Which transition corresponds to the emission of radiation maximum wavelength? (03)
MY YouTube Channel Link : 👉🖱 https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCGpC7nWE0-bBv9I53MM8qjQ
Atoms and Nuclei important questions, Atoms and Nuclei important questions, Atoms and Nuclei important questions, Atoms and Nuclei important questions, Atoms and Nuclei important questions, Atoms and Nuclei important questions