Atoms and Molecules Notes class 9
Hello readers ! Here supplementary class notes of Atoms and Molecules is given.
Antoine L. Lavoisier performed a number of chemical reactions and laid the foundation of chemical sciences. Antoine L. Lavoisier and Joseph L. Proust gives two important laws according to which chemical reactions take place, combinedly known as the laws of chemical combination.
Laws of Chemical Combination:
(1) Law of conservation of mass: Law of conservation of mass states that mass can neither be created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction. i.e. In a chemical reaction mass of reactant should be equal to mass of product.
For example: C + O2 → CO2 , here mass of carbon and oxygen (reactant) = mass of carbon dioxide (product)
(2) Law of constant proportions / Law of definite proportions: “In a chemical substance the elements are always present in definite proportions by mass”.
For example, In water, the ratio of the mass of hydrogen to the mass of oxygen is always 1:8, whatever the source of water. Thus, if 9 g of water is decomposed, 1 g of hydrogen and 8 g of oxygen are always obtained.
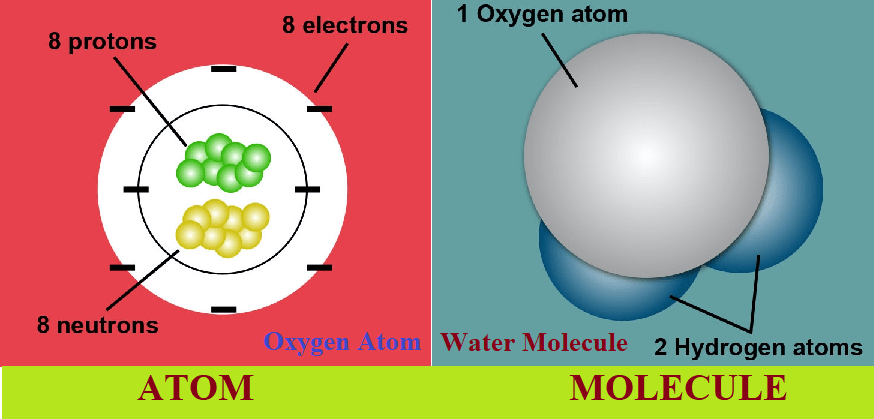
Table of Contents
Dalton’s atomic theory:
In 1808, John Dalton proposed an atomic theory known as Dalton’s atomic theory. According to the postulates of Dalton’s atomic theory,
(i) All matter is made of very tiny particles called atoms, which participate in chemical reactions.
(ii) Atoms are indivisible particles, which cannot be created or destroyed in a chemical reaction.
(iii) Atoms of a given element are identical in mass and chemical properties.
(iv) Atoms of different elements have different masses and chemical properties.
(v) Atoms combine in the ratio of small whole numbers to form compounds.
(vi) The relative number and kinds of atoms are constant in a given compound.
Atoms and Molecules Conceptual Questions
What is an atom?
Answer: An atom are the basic building block of matter. Atom is the smallest unit of an element that retains the chemical properties of that element. Atoms consists mainly protons, neutrons, and electrons.
What is the difference between molecules and compounds?
Answer: Difference between molecules and compounds,
| Molecules | Compounds |
|---|---|
| Two or more same or different type atoms/elements combined chemically to form molecule | Two or more different type atoms/elements combined chemically to form Compounds |
| All molecules are not compounds . | All compounds are molecules. |
| H2 , O2 , N2 etc. are molecules having same type of atoms/elements. H2O, CO2 etc. are molecules having different type of atoms/elements | Always contain different type atoms/elements H2O, CO2 etc. |
How are atoms and molecules related?
Answer: Atoms combine with other atoms to form molecules. Molecules are composed of two or more atoms held together by chemical bonds.
What are the main components of an atom?
Answer: There are three main components of an atom protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons have a positive charge, neutrons have no charge (they are neutral), and electrons have a negative charge. Protons and neutrons are located in the nucleus of the atom, while electrons orbit around the nucleus.
What is the atomic number of an atom?
Answer: The atomic number of an atom is equal to the number of protons in its nucleus. It determines the identity of the element. For example, hydrogen atoms have an atomic number of 1, carbon atoms have an atomic number of 6, and oxygen atoms have an atomic number of 8.
What is the mass number of an atom?
Answer: The mass number of an atom is the sum of the number of protons and neutrons in its nucleus. For example, if an atom has 6 protons and 6 neutrons, its mass number is 12.
Atoms and Molecules Notes class 9 , Atoms and Molecules Notes class 9 , Atoms and Molecules Notes class 9 , Atoms and Molecules Notes class 9 , Atoms and Molecules Notes class 9 , Atoms and Molecules Notes class 9 , Atoms and Molecules Notes class 9 , Atoms and Molecules Notes class 9 , Atoms and Molecules Notes class 9