Accuracy and Precision
Hello, readers 😊! Here you will learn about Accuracy and Precision. Precision and accuracy are two key ideas that are frequently misunderstood in the context of measurement and scientific research. Both have a connection to data quality, but they mean different things and have different implications. For academics, engineers, and anybody else looking for accurate and significant results, understanding the distinction between accuracy and precision is crucial.
Accuracy:
Accuracy measures how close a measured value is to the actual (true) value. Accuracy increases with a decrease in the least count of a measuring instrument.
For example: suppose we have to measure the thickness of a metallic sheet with different instruments like a metre scale, a Vernier calliper and a Screw-gauge. Each instrument has a different least count. For meter scale, the least count is 1 mm, 0.1 mm for Vernier calliper and 0.001 mm for Screwgauge. If we measure the thickness of the given metallic sheet using these instruments, then the measured value with a metre scale will be like 2 mm, 2.3 mm with Vernier calliper and 2.35 mm with Screwgauge. Among these measurements, the most accurate measurement is made by Screwgauge, as it has lowest least count and can measure 1/100th part of a milimeter easily.
So, lesser is the least count of measuring instruments, the more accurate will be the measurement.
Table of Contents
Precision:
Precision measures how close the measured values are to each other.
Assume you go to the market and purchase 1.500 kg (true value) of paneer. You weigh paneer again after returning home, and your findings are 1.460 kg, 1.453 kg, 1.462 kg, 1.515 kg, and 1.455 kg. Here, the majority of the readings, for the four observations (1.453 kg, 1.462 kg, 1.460 kg, and 1.455 kg) are close to each other but not equal or close to the true value in your recorded observations at home. Your measurement is very precise but not accurate. Precision is independent of accuracy. A measurement may be precise but not accurate.
Understanding Accuracy and Precision with the help of analogy:
To better comprehend the disparity between accuracy and precision, consider the following analogy:
Imagine a skilled archer aiming at a target. If the archer consistently hits the bullseye, the shots are both accurate and precise.
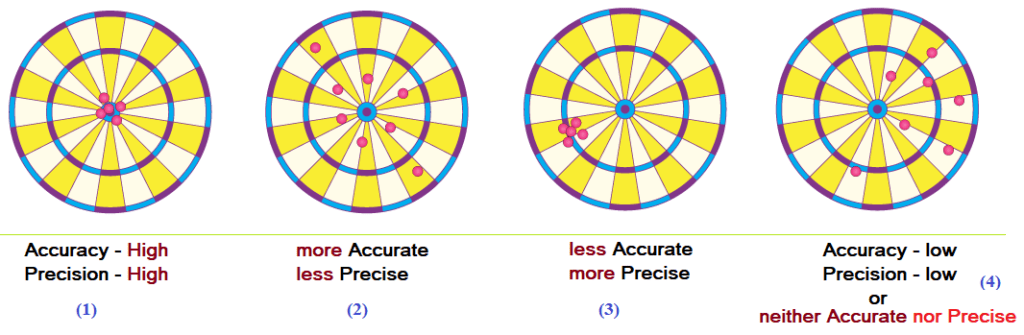
- If you hit an arrow to the bull’s-eye center (1st figure), then you are accurate. Accuracy is how close a measured value is to its true value.
- If you repeatedly hit the arrow in the same spot without scoring or scoring less (3rd figure), you are not accurate or less accurate, but you are precise!
Remember, accuracy gets you close to the bullseye, while precision keeps your shots tightly grouped.
Applications of concept of Accuracy and Precision:
Accuracy and precision are terms used to express the quality of measurement in physics, engineering, statistics, and other fields.
Accuracy and precision play pivotal roles in maintaining high-quality standards. Industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics rely on accurate measurements to ensure components and products meet specifications. Precision, in terms of consistency, helps identify variations and defects in production, allowing for adjustments and improvements to optimize output quality.
Difference between Accuracy and Precision
| parameter | Accuracy | Precision |
| Quality: | Doesn’t speak about quality | Speaks of quality of product |
| Measurements: | may be a single measurement | A number of measurements are needed |
| Error | Accuracy indicates the absence of systematic errors. | Precision reflects the absence of random errors. |
Questions from Accuracy and Precision
Important MCQ
Q.1: While performing an experiment, a student measures the depth of a beaker with the help of Vernier calipers. He recorded observations of 8.21 cm, 8.19 cm, 8.20 cm, and 8.20 cm in the first, second, third, and fourth trials, respectively. The true value of the depth of the beaker is 8.10. Which of the following statements is true about his measurements?
[A] They are neither precise nor accurate
[B] They have poor accuracy
[C] They have good precision
[D]They have poor precision.
[C] They have good precision
Question 2:
What do you mean by accuracy?
Ans: Accuracy measures how close a measured value is to the actual (true) value.
Question 3:
What do you mean by precision ?
Ans: Precision measures how close the measured values are to each other.
Question 4:
What is the difference between accuracy and precision?
Answer: Accuracy relates to how close a measurement is to the true value, while precision focuses on the consistency and repeatability of measurements, irrespective of their proximity to the true value. Accuracy indicates the absence of systematic errors, while precision reflects the absence of random errors.
MY YouTube Channel Link : 👉🖱 https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCGpC7nWE0-bBv9I53MM8qjQ
