Acceleration
Table of Contents
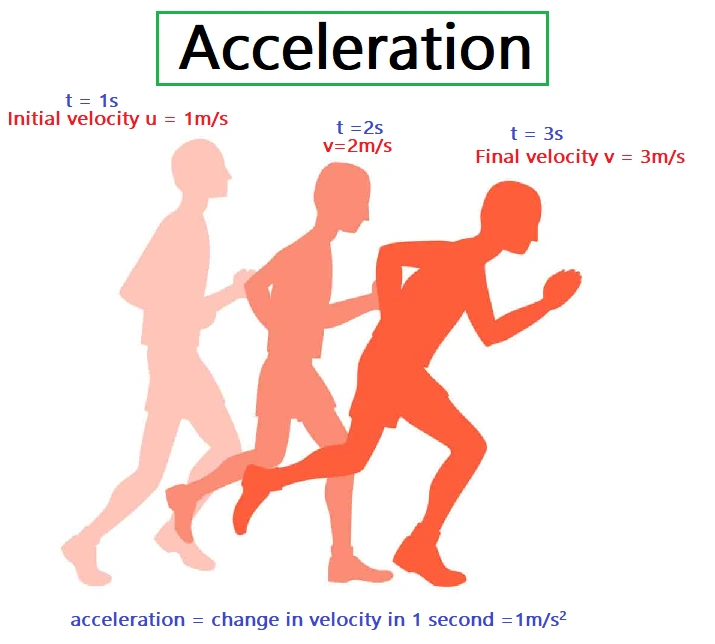
- The rate of change of velocity is known as acceleration.
- It is a vector quantity.
- Acceleration (a) = Change in velocity (v–u) / time taken (t)
- SI Unit = meter/second² ( m/s²)
Significance of Acceleration:
The acceleration of a moving body measures how much the velocity of a body changes in one second. If the change in speed of the body is positive, the body is accelerating, and if the change in speed is negative, the body is decelerating.
Retardation:
- The acceleration taken as negative is known as deceleration or retardation.
- In acceleration, speed of body increases while in deceleration speed of body decreases.

Some important short answer type questions:
Questions 1:
What do you mean by negative acceleration?
Answer : If direction of acceleration is opposite to the direction of velocity, then body have negative acceleration. For example: When we apply break there is negative acceleration or retardation.
Questions 2:
Is it possible that a body moving at a constant speed is still accelerating?
Answer: Yes, if a body is moving in a circular path, its speed may be constant, but due to a change in direction, its velocity changes, and hence the body accelerates.
What is acceleration?
Answer: Acceleration refers to the rate at which an object’s velocity changes over time. It is a vector quantity that takes into account both the magnitude and direction of the change in velocity.
How is acceleration calculated?
Answer: Acceleration can be calculated by dividing the change in velocity by the time taken for that change to occur. The formula for acceleration is: acceleration = (final velocity – initial velocity) / time.
What are the units of acceleration?
Answer: The units of acceleration depend on the system of measurement being used. In the International System of Units (SI), acceleration is measured in meters per second squared (m/s²).
What is positive acceleration?
Answer: Positive acceleration occurs when an object’s velocity increases over time. It means that the object is moving in the same direction as its velocity vector.
What is the difference between acceleration and retardation?
Answer: Acceleration refers to the rate of change of velocity, either positive or negative, indicating an increase or decrease in speed. On the other hand, retardation is synonymous with negative acceleration and represents the rate at which an object’s velocity decreases over time.
What is the relationship between acceleration and force?
Answer: According to Newton’s second law of motion, the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force applied to it and inversely proportional to its mass. The formula is: acceleration = net force / mass. Thus, a larger force applied to an object will result in a greater acceleration, while a smaller force will lead to a smaller acceleration.
Can a body possess constant speed but variable velocity?
Answer: Yes, if body is in uniform motion either on circular path or curved path then it’s speed will be constant but changing velocity.
Since velocity is a vector quantity so it can be changed either by changing magnitude or direction.
How is the distance traveled by a freely falling object related to time?
Answer : The distance traveled by a freely falling object is directly related to the square of the time. In other words, the distance is proportional to the square of the time squared (d ∝ t²).
Can objects of different masses fall at different rates?
Answer : In the absence of air resistance, objects of different masses will fall at the same rate. This is known as the principle of equivalence or the “Galileo’s experiment.” However, in real-world scenarios with air resistance, the rate of fall can vary for objects with different masses and surface areas.
A stone is dropped from a height of 50m and it falls freely. Calculate the (i) distance travelled in 2 s, (ii) velocity of the stone when it reaches the ground, and (iii) velocity at 3 s i.e., 3 s after the start.
Ans: Given: u = 0 (Since body is dropped)
(i) Distance travelled, x = ? at t = 2s
from equation of motion (2) x = ut + ½ at2
x = 0 + 0 – ½ gt2 = –½ × 9.8 × (2)2
= –19.6 m
ii) At the ground S = – 50m,
Using equation of motion (3),
v2 = u2 + 2a S
= 0 + 2 (–9.8) (–50 )
v = 9.9 m/s
iii) Using v = u + at, at t = 3s, we get
∴ v = 0 + (–9.8) × 3
v = –29.4 m/s
Pages
MY YouTube Channel Link : 👉🖱 https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCGpC7nWE0-bBv9I53MM8qjQ