4 Basic Natural Forces
Hello, readers 😊! Here you will learn about ‘4 Basic Natural Forces/Fundamental Forces in Nature’, their cause, properties and formula.
There are 4 Basic Natural Forces in nature that govern the interactions between particles and objects. These forces are:
- Gravitational Force (FG)
- Weak Nuclear Force (FWN)
- Electromagnetic Force (FE)
- Strong Nuclear Force (FSN)
These four fundamental forces play a crucial role in shaping the behavior of matter and the interactions between particles at both microscopic and cosmic scales. Scientists have been able to describe and understand many natural phenomena by studying these forces and their effects.
Table of Contents
Relative strength of Fundamental Forces in Nature
FG : FWN : FE: FSN = 1: 1025 :1036 : 1038
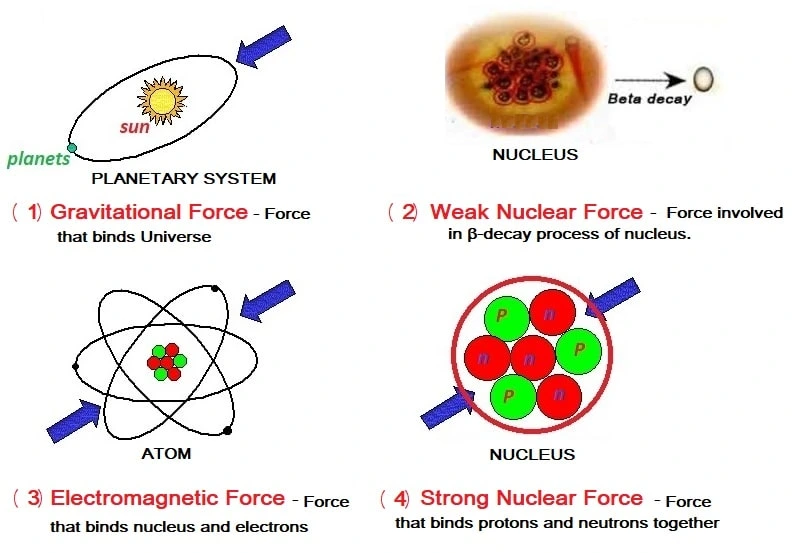
(1) Gravitational Force (FG):
The force of attraction between any two masses in the universe is called Gravitational Force.
It is given by Newton’s law of Gravitation. According to this law, Gravitational force of attraction between two bodies is directly proportional to product of their masses and inversely proportional to square of separation between them.
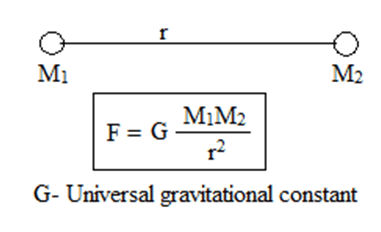
Characteristics of Gravitational force:
- Gravitational force is the weakest force in nature.
- It is a conservative force.
- Gravitational force is always attractive in nature.
- Gravitational force is a mutual force and it obey Newton’s III Law i.e. The amount of force with which the earth attracts an object is equal to the attractive force applied by the object on earth.
The gravitational force of the earth on an object = The gravitational force of the object on the earth
- It is a long-range force. Planets are far away from the sun and move under the gravitational force of the sun
(2) Weak Nuclear Force (FWN):
Force acting between elementary particle (between electron and neutrino) involved in β-decay of a nucleus.
- Very short range force (=10-15 m)
- Any process involving neutrino and antineutrino is govern by this force.
(3) Electromagnetic Force (FE):
Force acting between two charges at rest or two magnetic substance/ moving charge.
The force between two charges can be calculated by Coulomb’s law. According to this law electrostatic force acting between two charges is directly proportional to product of magnitude of their charges and inversely proportional to square of separation between them.
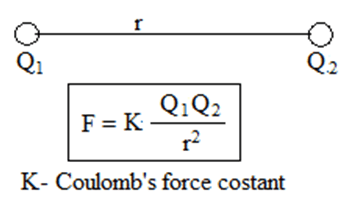
Where K is Electrostatic force constant. K = 9 x 109 Nm2/C2 q1 and q2 are magnitude of two charges.
Characteristics of Electromagnetic force:
- It is conservative in nature.
- It is a long range force.
- It obey Newton’s III Law.
- It is a central force – a charged body attracts another charged body towards its centre.
- It may be Attractive or repulsive in nature
(4) Strong Nuclear Force (FSN):
Strong attractive force which binds together protons and neutrons in nucleus.
- It is charge independent force.
- It is non-central and non-conservative force.
- It is a short range force (few fm).
Video Lecture on topic Fundamental Forces in Nature
This video lectures contains topics: Fundamental Forces in Nature and their Relative strength, Four basic Conservation Law.
4 basic Conservation Law
There are 4 basic Conservation Laws in nature,
- Law of conservation of energy: This law states that energy can neither be created nor be destroyed but it can changed from one form to another ie. Total Energy of system is always conserved.
- Law of conservation of linear momentum: If there is no external force applied on the system total linear momentum of the system remains conserved.
- Law of conservation of angular momentum: : If there is no external torque applied on the system total angular momentum of the system remains conserved
- Law of conservation of charge: Total charge of an isolated system remains conserved. Net charge can neither be produced nor be destroyed
Questions and Answers based on Topic
What are the 4 basic natural forces?
The 4 basic natural forces are gravitational force, electromagnetic force, strong nuclear force, and weak nuclear force.
What is gravitational force?
Gravitational force is a force of attraction that exists between any two objects with mass.
What is electromagnetic force?
Electromagnetic force is a fundamental force that arises from the interaction of electrically charged particles.
What is strong nuclear force?
Strong nuclear force is the fundamental force that holds atomic nuclei together.
What is weak nuclear force?
Weak nuclear force is responsible for certain types of radioactive decay.
How do the four basic natural forces differ from each other?
The four basic natural forces differ in terms of their range, strength, and the particles they act upon. For example, gravitational force is the weakest but has an infinite range, while strong nuclear force is the strongest but only acts within the atomic nucleus.
MY YouTube Channel Link : 👉🖱 https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCGpC7nWE0-bBv9I53MM8qjQ
4 Basic Natural Forces, 4 Basic Natural Forces, 4 Basic Natural Forces, 4 Basic Natural Forces, 4 Basic Natural Forces, 4 Basic Natural Forces, 4 Basic Natural Forces, 4 Basic Natural Forces